1.
alert(1=='1') // true
alert(1==='1') // false2.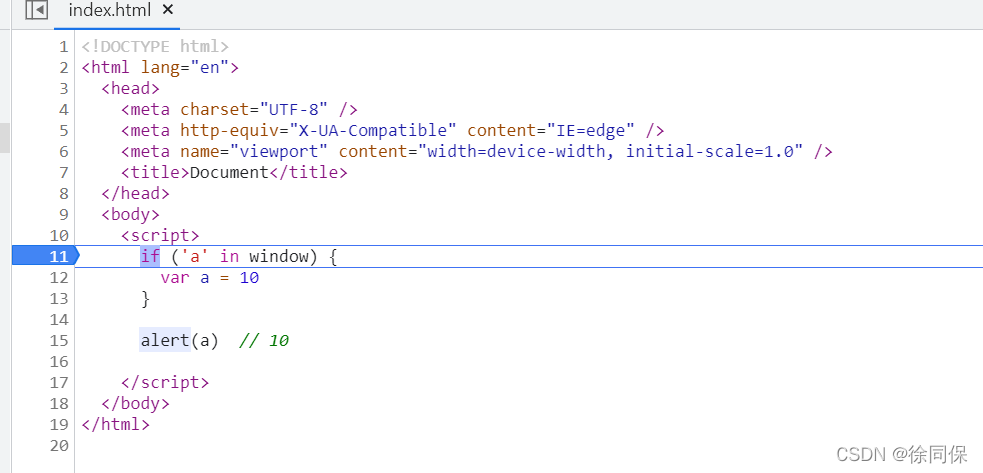

if ('a' in window) {
var a = 10
}
alert(a) // 103.

num = 123
function fun1() {
var num = 123
return num++
}
fun1()
alert(num) // 1234.
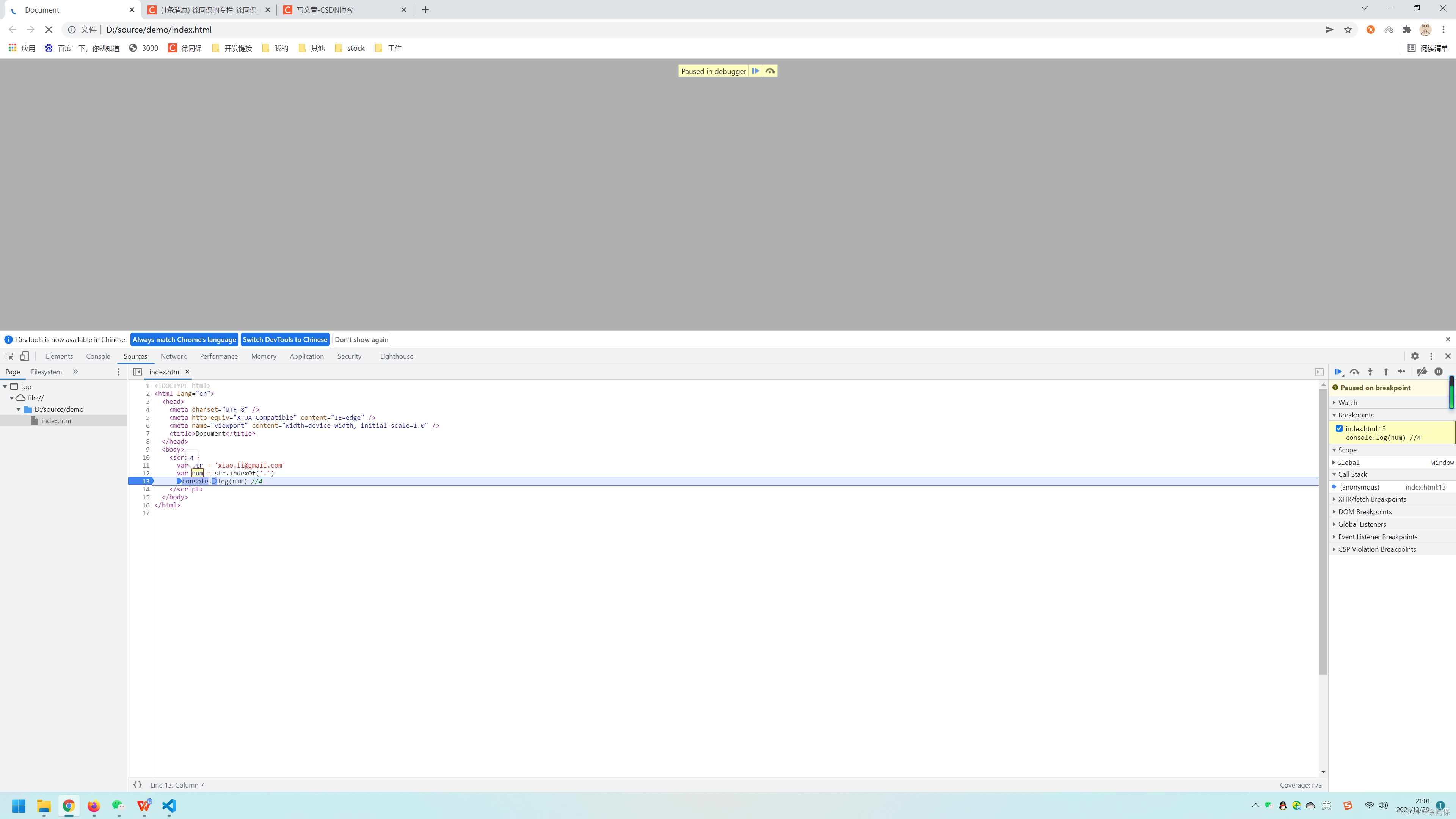
var str = 'xiao.li@gmail.com';
var num=str.indexOf('.')
console.log(num) //45.

var msg = 'hello'
for (var i = 0;i < 10; i ++) {
var msg = 'hello' + i * 2 + i
}
console.log(msg) //hello1896.
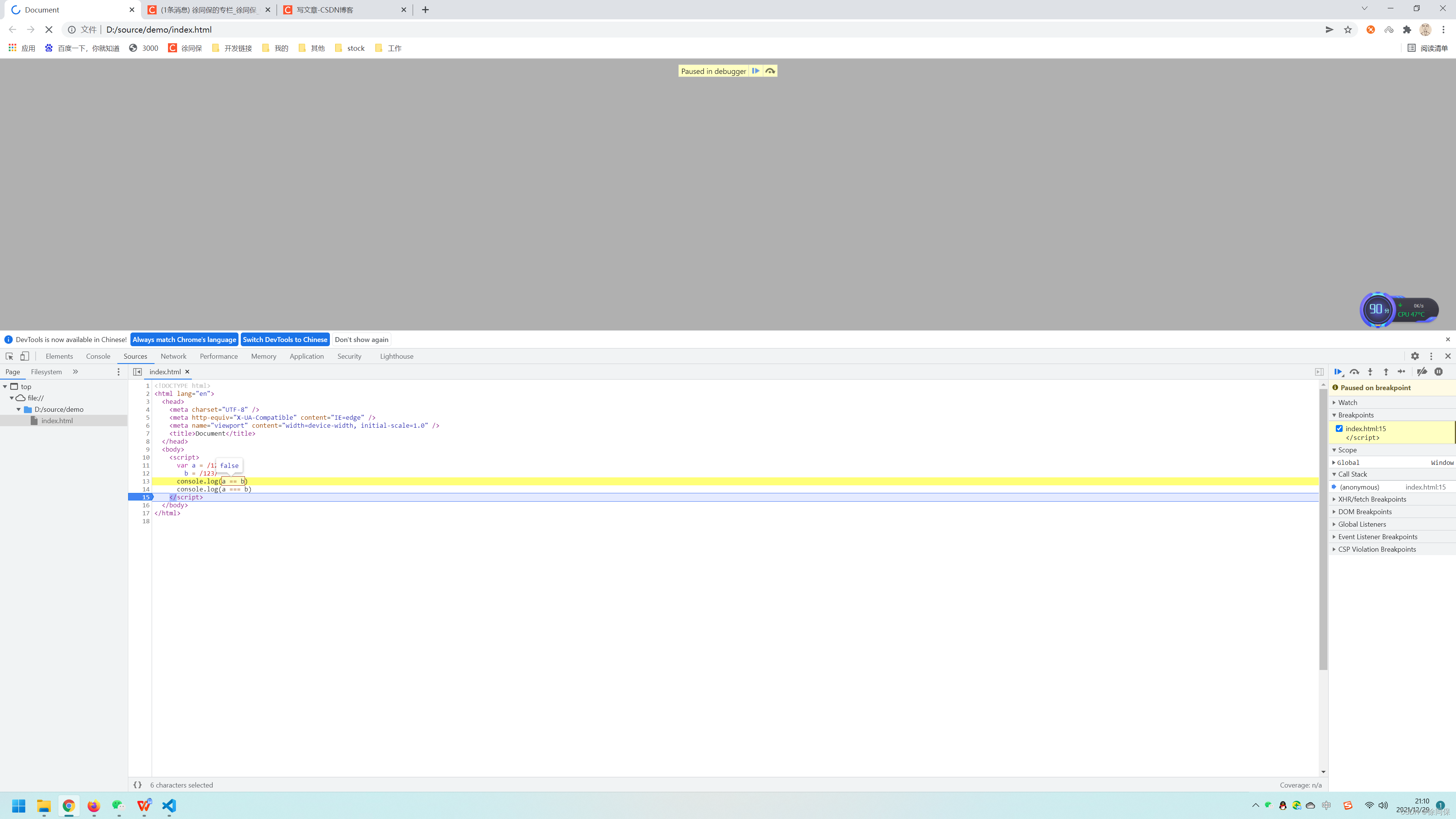

var a = /123/,
b = /123/
console.log(a == b) //false
console.log(a === b) //false7.
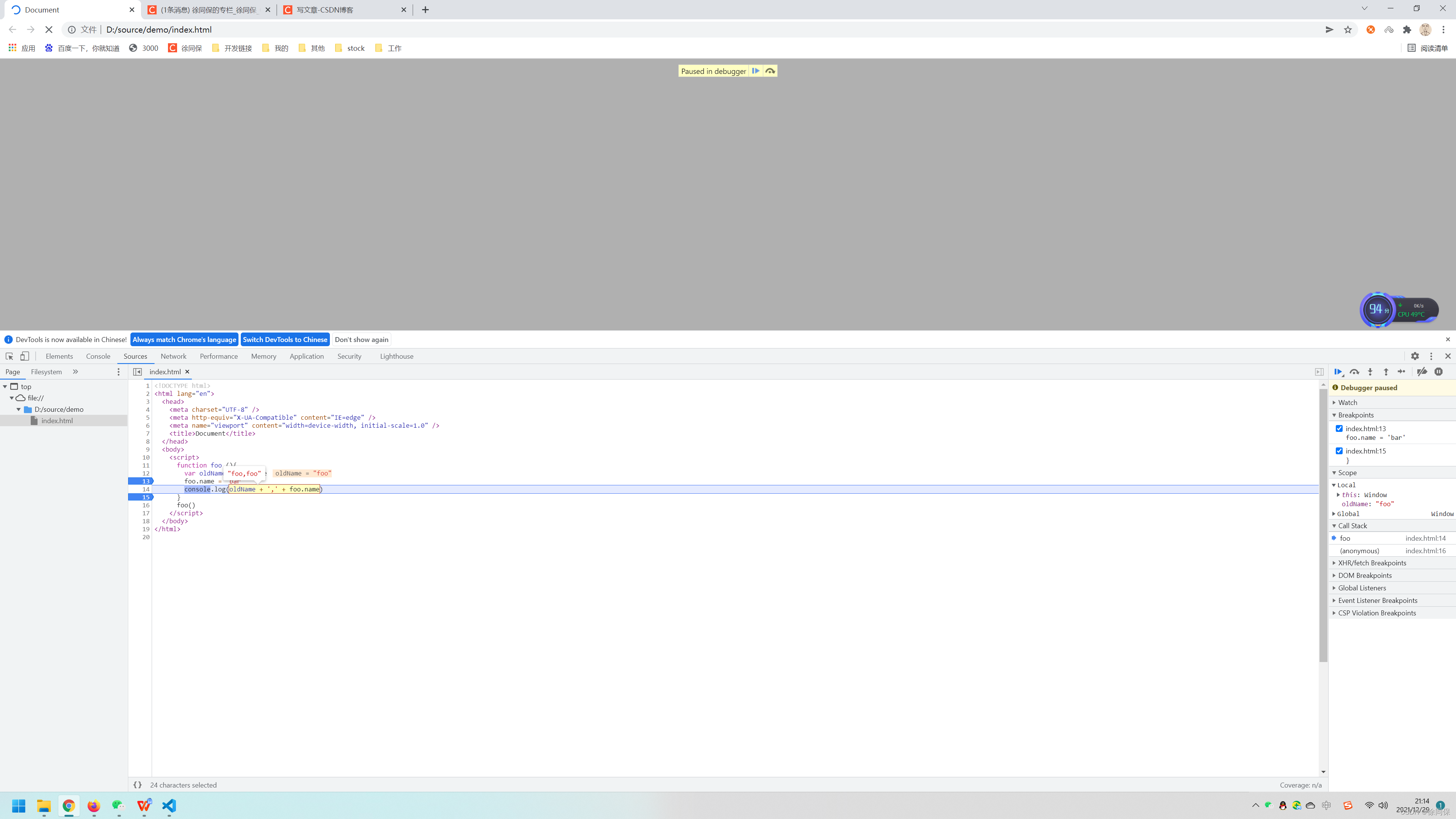
function foo (){
var oldName = foo.name
foo.name = 'bar'
console.log(oldName + ',' + foo.name) //foo,foo
}
foo()8.
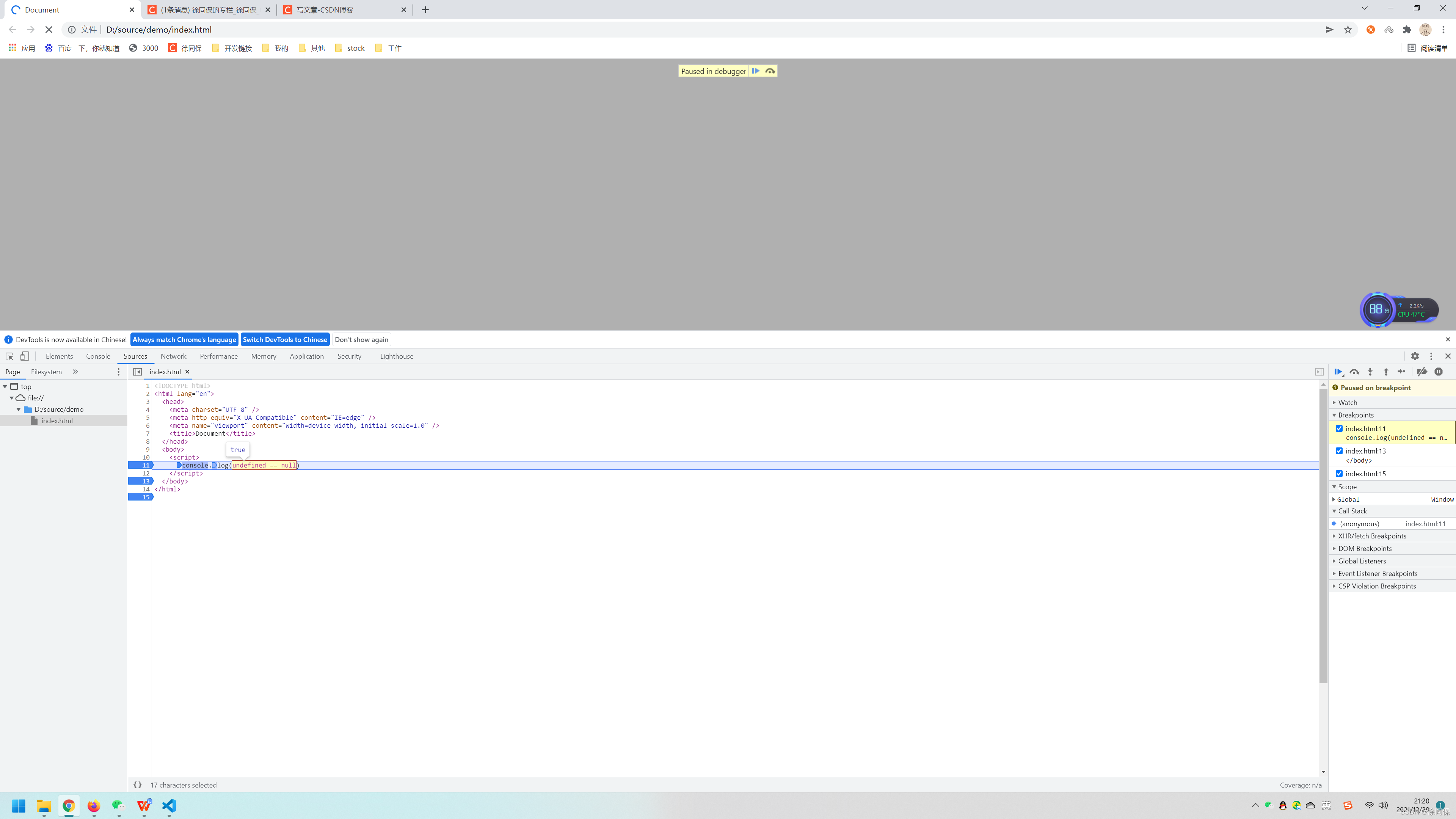
console.log(undefined == null) // true9.

var emp = new Array(5)
emp[1] = 1
emp[2] = 3
console.log(emp.length) // 510.
num = 123
function fun1() {
var num = 123
return num++
}
fun1()
console.log(num) //12311.
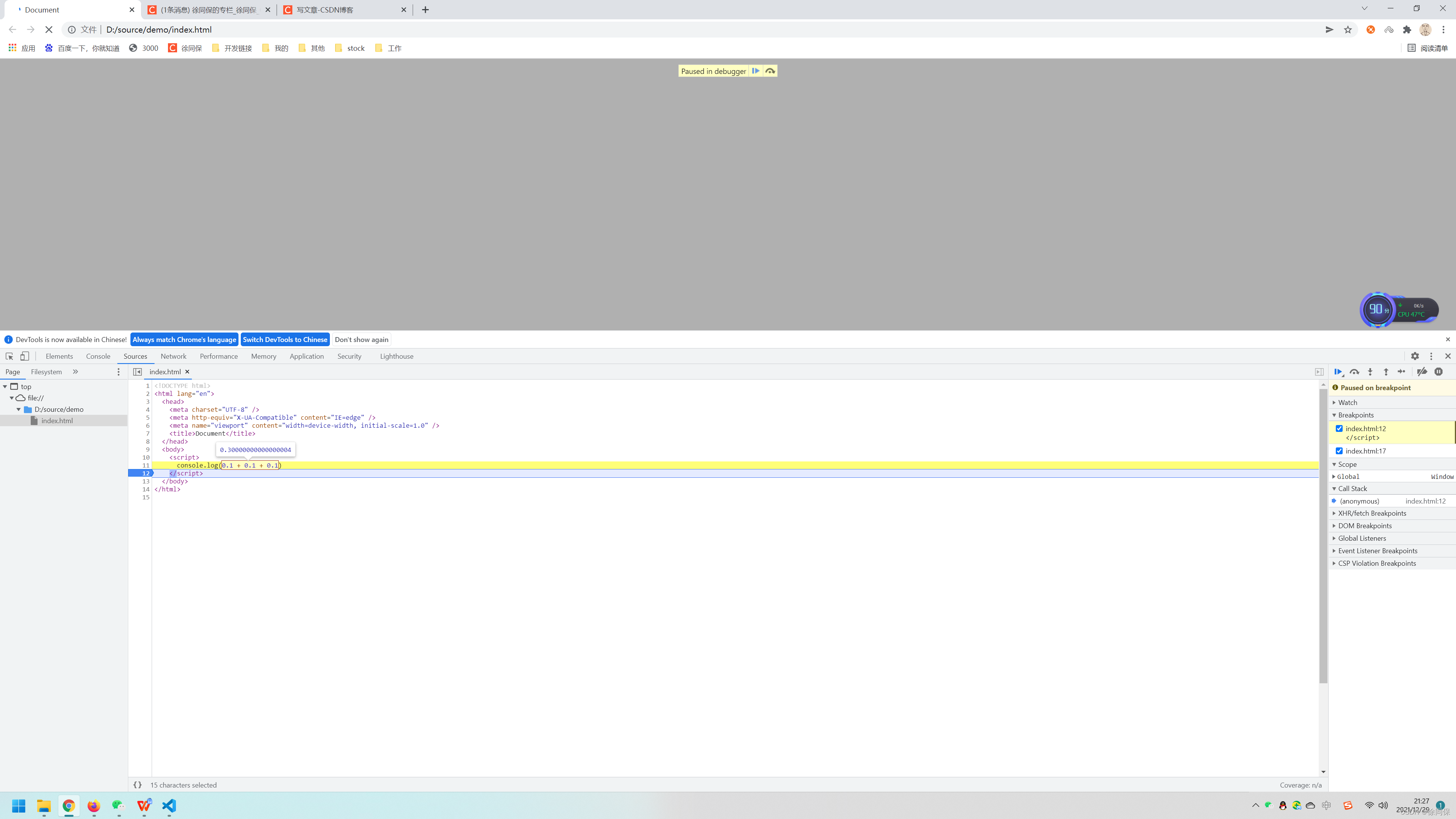
console.log(0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1) //0.3000000000000000412.
HTTP协议、TCP协议、IP协议分别在应用层,传输层,网络层
13.
const obj = { 1: "a", 2: "b", 3: "c" };
const set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty("1")) //true
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty(1)) //true
console.log(set.has("1")) //false
console.log(set.has(1)) //true14.
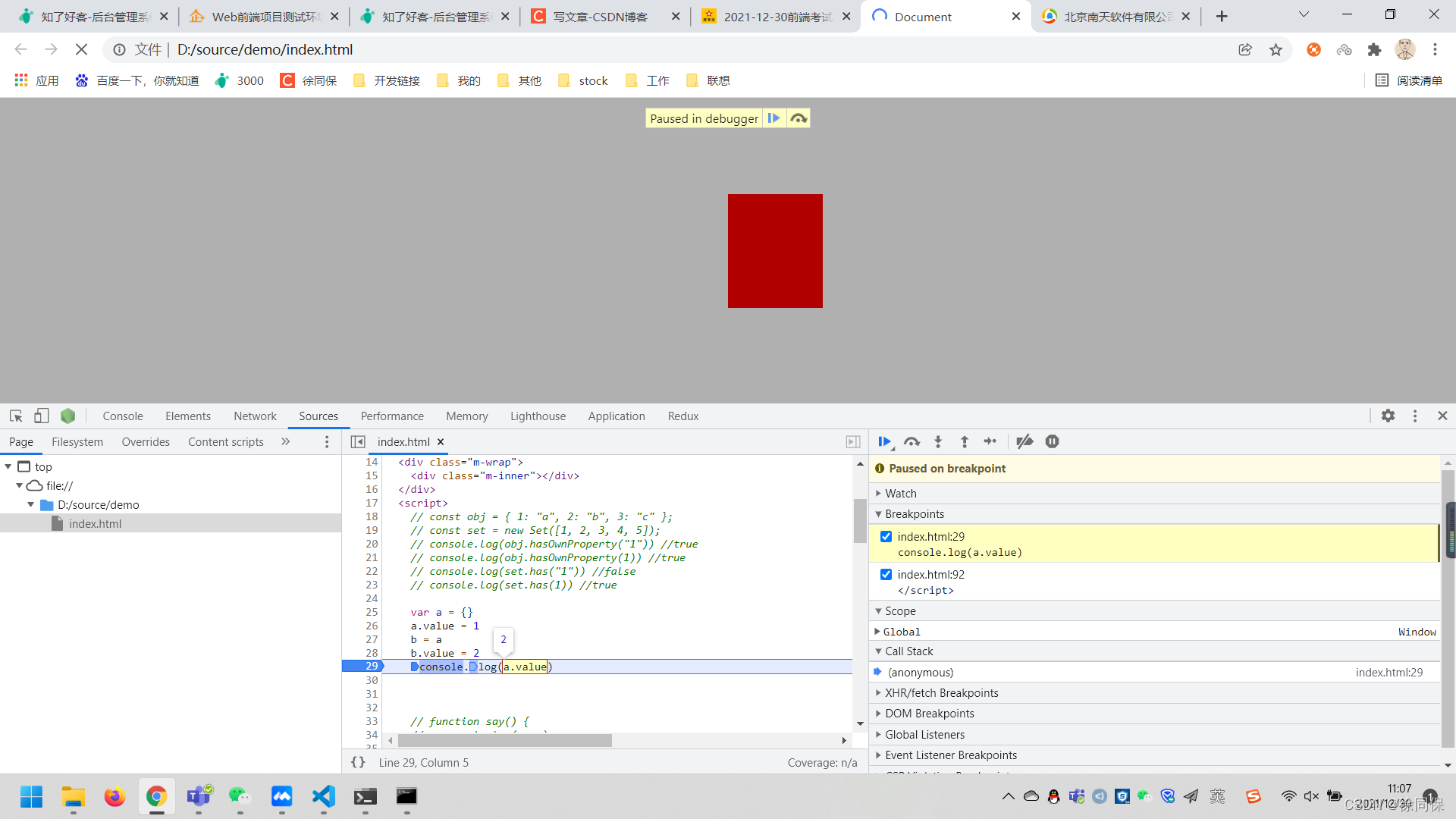
var a = {}
a.value = 1
b = a
b.value = 2
console.log(a.value) //215.
function say() {
console.log(name) //undefined
console.log(age) //报错
var name = 'TJH'
let age = 24
}
say()16.
function Foo () {
getName = function () {
console.log(1)
}
return this
}
Foo.getName = function () {
console.log(2)
}
Foo.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(3)
}
var getName = function() {
console.log(4)
}
function getName() {
console.log(5)
}
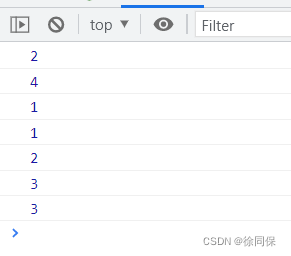
Foo.getName() //2
getName() //4
Foo().getName() //1
getName() //1
new Foo.getName() //2
new Foo().getName() //3
new new Foo().getName() //317.
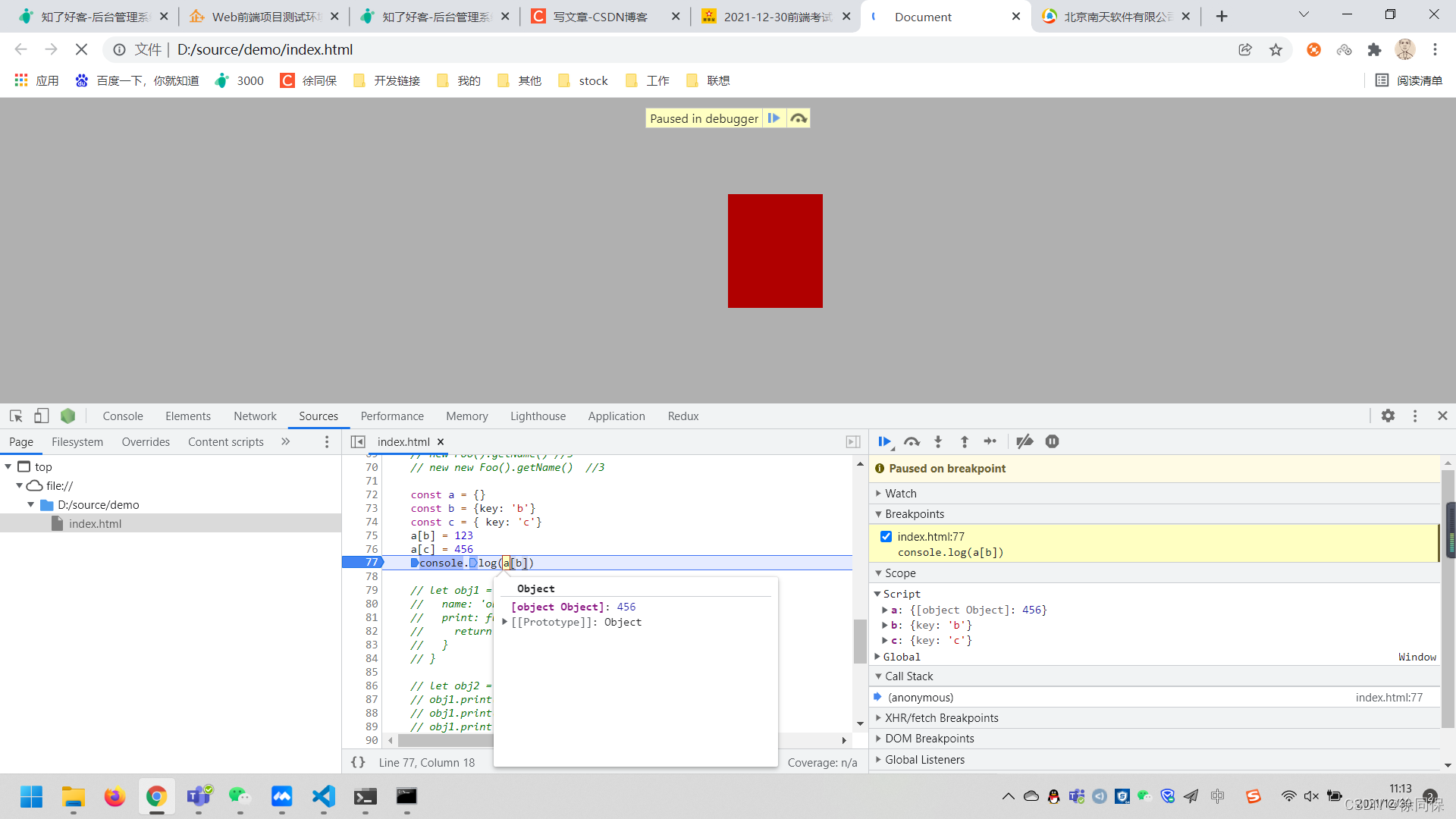
const a = {}
const b = {key: 'b'}
const c = { key: 'c'}
a[b] = 123
a[c] = 456
console.log(a[b]) //45618.
let obj1 = {
name: 'xu',
print: function () {
return () => console.log(this.name)
}
}
let obj2 = {name: "tongbao"}
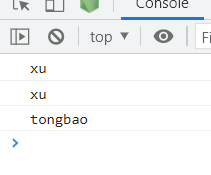
obj1.print()() //xu
obj1.print().call(obj2) //xu
obj1.print.call(obj2)() //tongbao










