文章目录
- tensorflow数据类型
- 创建Tensor
- 索引操作
- 维度变换
- Broadcasting
- 数学运算
- 前向传播
- 合并与分割
- 数据统计
- 张量排序
- 填充与复制
- 张量限幅
- 高阶op
- 数据加载
- 测试 (张量) 实战
- 全连接层
- 输出方式
- 误差计算
- 梯度计算
- 函数优化实战
tensorflow数据类型
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test1.ipynb
创建Tensor
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test2.ipynb
索引操作
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/bj/blob/master/tensor_test3.ipynb
维度变换
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/bj/blob/master/tensor_test4.ipynb
Broadcasting
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test5.ipynb
数学运算
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test6.ipynb
前向传播
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets
import os
os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"] = '2'
# x: [60k,28,28],
# y: [60k]
# 加载数据集
(x, y), _ = datasets.mnist.load_data()
# 转换成tensor形式
# x:[0~255] => [0~1.] # 便于deep learning 优化
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32)
# print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x))
# print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y))
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)).batch(128)
train_iter = iter(train_db)
sample = next(train_iter)
# (128, 28, 28) (128,)
print("batch:", sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
# [dim_in, dim_out], [dim_out]
# 截断正态分布 方差0.1
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256]))
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128]))
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
lr = 1e-3
# iterate db for 10
for epoch in range(10):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): # for every batch
# x: [128, 28, 28]
# y: [128]
# x: [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
# 只能跟踪 tf.Variable 类型
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# x: [b, 28*28]
# h1 = x@w1 + b1
# [b, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [256]
h1 = x@w1 + b1
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1)
# [b, 256] => [b, 128]
h2 = h1@w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2)
# [b, 128] => [b, 10]
out = h2@w3 + b3
# compute loss
# out: [b, 10]
# y: [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2)
# square平方
# [b, 10]
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out)
# mean: scalar
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
# compute gradients
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])
# w1 = w1 - lr * grads[0]
# 原地更新
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1])
w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2])
b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3])
w3.assign_sub(lr * grads[4])
b3.assign_sub(lr * grads[5])
if step % 100 == 0:
print("epoch",epoch,"step",step, 'loss:', float(loss))合并与分割
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test7.ipynb
数据统计
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test8.ipynb
张量排序
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test9.ipynb
填充与复制
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test10.ipynb
张量限幅
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test11.ipynb
高阶op
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test12.ipynb
数据加载
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test13.ipynb
测试 (张量) 实战
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets
import os
os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"] = '2'
# x: [60k,28,28], [10,28,28]
# y: [60k]
# 加载数据集
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
# 转换成tensor形式
# x:[0~255] => [0~1.] # 便于deep learning 优化
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32)
x_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_test, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(y_test, dtype=tf.int32)
# print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x))
# print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y))
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)).batch(128)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).batch(128)
train_iter = iter(train_db)
sample = next(train_iter)
# (128, 28, 28) (128,)
print("batch:", sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
# [dim_in, dim_out], [dim_out]
# 截断正态分布 方差0.1
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256]))
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128]))
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
lr = 1e-3
# iterate db for 10
for epoch in range(100):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): # for every batch
# x: [128, 28, 28]
# y: [128]
# x: [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
# 只能跟踪 tf.Variable 类型
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# x: [b, 28*28]
# h1 = x@w1 + b1
# [b, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [256]
h1 = x@w1 + b1
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1)
# [b, 256] => [b, 128]
h2 = h1@w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2)
# [b, 128] => [b, 10]
out = h2@w3 + b3
# compute loss
# out: [b, 10]
# y: [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2)
# square平方
# [b, 10]
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out)
# mean: scalar
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
# compute gradients
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])
# w1 = w1 - lr * grads[0]
# 原地更新
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1])
w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2])
b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3])
w3.assign_sub(lr * grads[4])
b3.assign_sub(lr * grads[5])
if step % 100 == 0:
print("epoch", epoch, "step", step, 'loss:', float(loss))
# test/evluation
# [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]
total_correct, total_num = 0, 0
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(test_db):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
h1 = tf.nn.relu(x@w1 + b1)
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h1@w2 + b2)
out = h2@w3 + b3
# out: [b, 10] ~ R
# prob [b, 10] ~ [0, 1]
# 映射到0~1的范围内
prob = tf.nn.softmax(out, axis=1)
# [b, 10] => [b]
# int64!!!!
# 返回axis=1维度上最大值对应的索引
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# y: [b]
# [b], int32
correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y), dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct)
total_correct += int(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]
# 计算准确率
acc = total_correct / total_num
print("accu:",acc)全连接层
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test14.ipynb
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# [batch, data]
x = tf.random.normal([2, 5])
# 指定每一层的神经元个数和激活函数
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(2)
])
# 指定模型的输入的维度
model.build(input_shape=[None, 5])
# 输出每一层的网络结构
model.summary()
# 显示每一层训练的参数和参数的shape
for p in model.trainable_variables:
print(p.name, p.shape)
# dense/kernel:0 (5, 2)
# dense/bias:0 (2,)
# dense_1/kernel:0 (2, 2)
# dense_1/bias:0 (2,)
# dense_2/kernel:0 (2, 2)
# dense_2/bias:0 (2,)输出方式
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test15.ipynb
误差计算
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test16.ipynb
梯度计算
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/sweetheart-7-7/whb/blob/master/tensor_test17.ipynb
函数优化实战
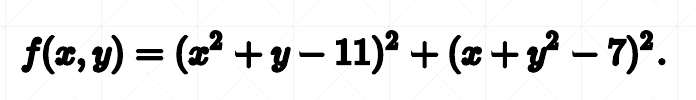
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
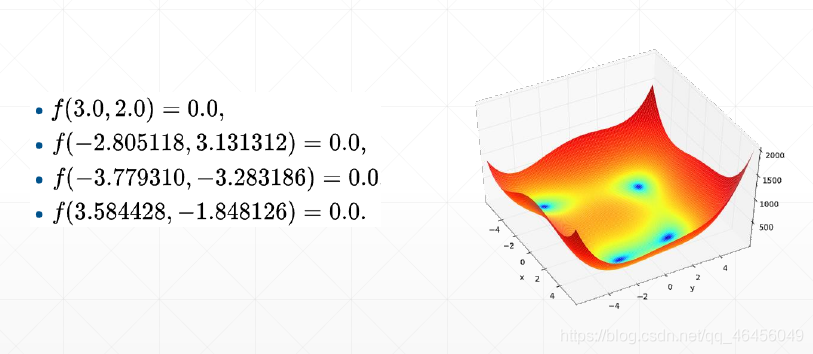
def fn(x):
return (x[0] ** 2 + x[1] - 11) ** 2 + (x[0] + x[1] ** 2 - 7) ** 2
x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
y = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
print("x,y range:", x.shape, y.shape)
# 生成网格数据
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print("X,Y maps:", X.shape, Y.shape)
Z = fn([X, Y])
# 获取到当前figure对象
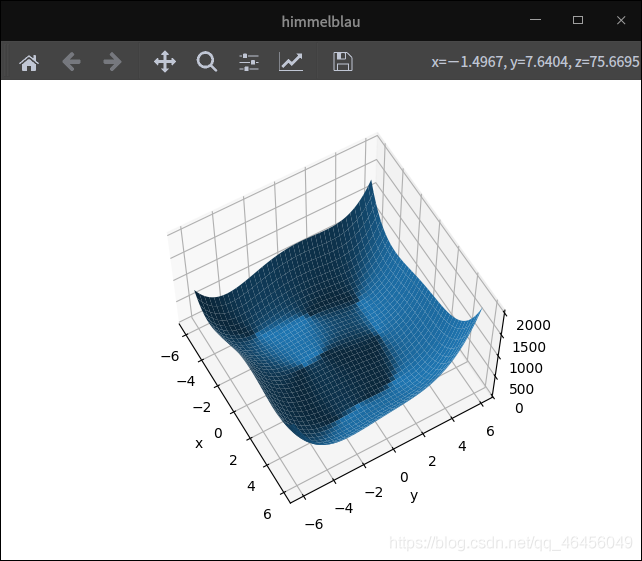
fig = plt.figure("himmelblau")
# 获取图中的当前极轴。如果不存在,或者不是极轴,则将创建相应的轴,然后返回。
# 此时得到的ax对象的类型是Axes3D的子类,这个对象将是绘制3D图形的入口
ax = fig.gca(projection="3d")
# 为了绘制 3D 图形,需要调用 Axes3D 对象的 plot_surface()方法来完成。
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
# 转换视角进行观察
ax.view_init(60, -30)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
plt.show()
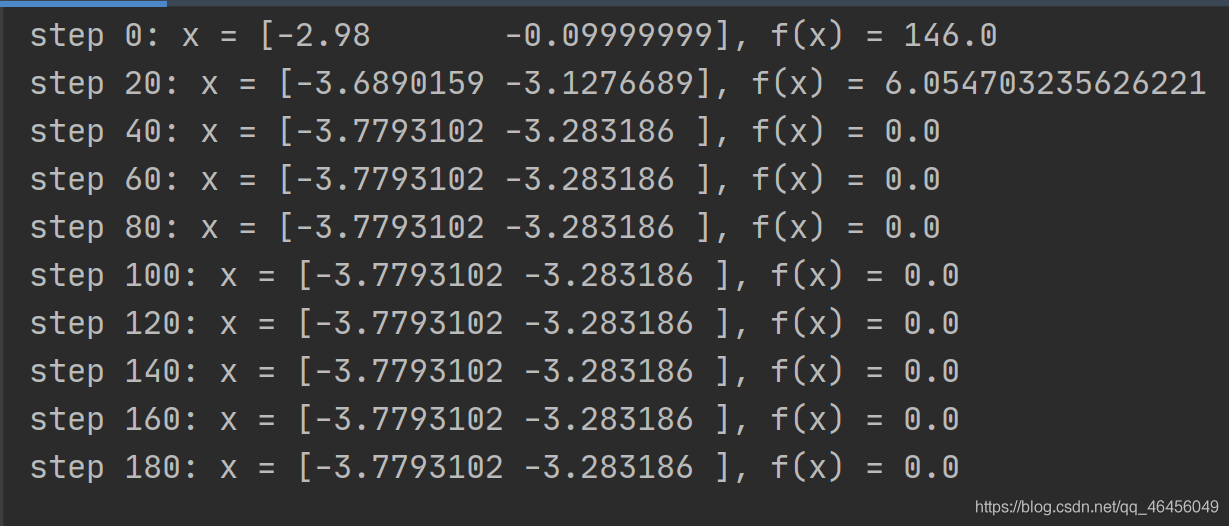
x = tf.constant([-4., 0.])
for step in range(200):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([x])
y = fn(x)
grads = tape.gradient(y, [x])[0]
x -= 0.01 * grads
if step % 20 == 0:
print("step {}: x = {}, f(x) = {}".format(step, x.numpy(), y.numpy()))