目录
一、什么是依赖注入
二、依赖注入方式
1. Setter注入
被注入类编写属性的setter方法
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao){
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
配置文件中,给需要注入属性值的 <bean> 中设置 <property>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"> </bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!--依赖注入-->
<!--name:对象的属性名 ref:容器中对象的id值-->
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property>
</bean>
测试
新增测试方法
// 测试依赖注入
@Test
public void t6(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
StudentService service = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
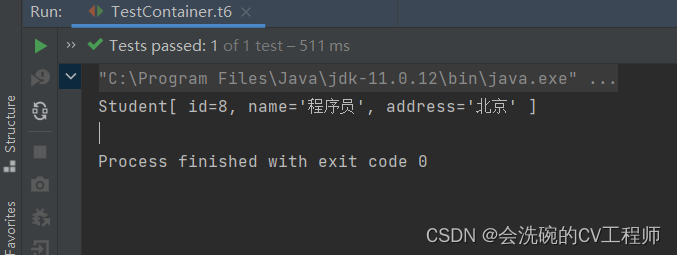
System.out.println(service.findStudentById(8));
}运行结果
2. 构造方法注入
被注入类编写有参的构造方法
public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao){
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
给需要注入属性值的 <bean> 中设置 <constructor-arg>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 依赖注入 -->
<!-- name:对象的属性名 ref:配置文件中注入对象的id值 -->
<constructor-arg name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></constructor-arg>
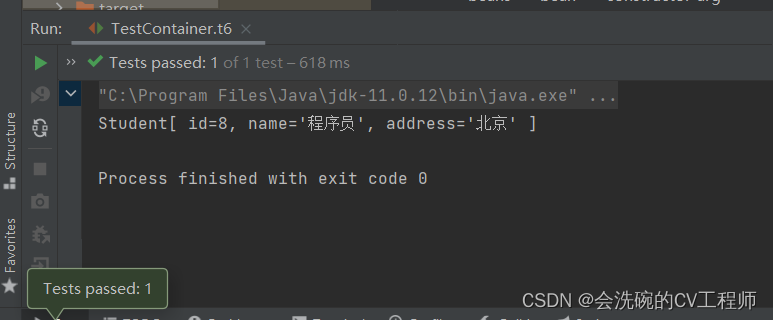
</bean>测试结果:
3. 自动注入
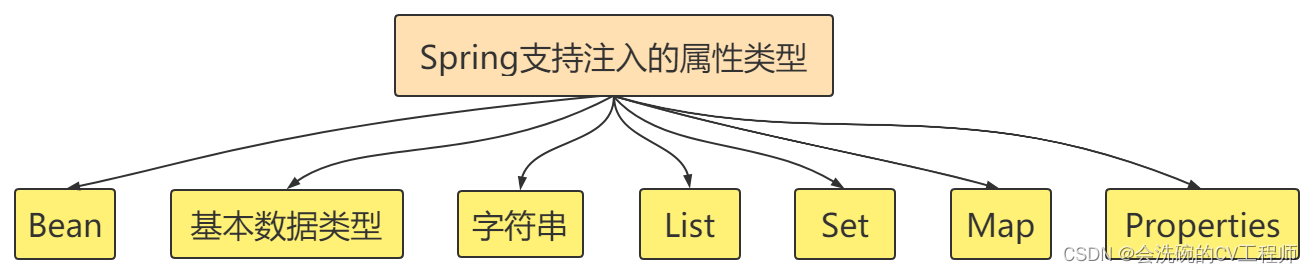
三、依赖注入类型
准备注入属性的类
package com.example.service;
import com.example.dao.StudentDao;
import com.example.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class StudentService {
// service依赖dao,手动注入属性值,即手动维护依赖关系
//private StudentDao studentDao;
// bean属性
private StudentDao studentDao;
// 字符串类型
private String name;
// 基本数据类型
private int count;
// 字符串List集合
private List<String> students1;
// 对象类型List集合
private List<Student> nameList;
// 字符串类型Set集合
private Set<String> students2;
// 字符串类型Map集合
private Map<String, String> students3;
// 对象类型map集合
private Map<String,Student> studentMap;
// Properties类型
private Properties properties;
public StudentService(){}
public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao){
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public Student findStudentById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao){
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public StudentDao getStudentDao() {
return studentDao;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public List<String> getStudents1() {
return students1;
}
public void setStudents1(List<String> students1) {
this.students1 = students1;
}
public Set<String> getStudents2() {
return students2;
}
public void setStudents2(Set<String> students2) {
this.students2 = students2;
}
public Map<String, String> getNames2() {
return students3;
}
public void setNames2(Map<String, Student> names2) {
this.studentMap = names2;
}
public Map<String, String> getStudents3() {
return students3;
}
public void setStudents3(Map<String, String> students3) {
this.students3 = students3;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public List<Student> getNameList() {
return nameList;
}
public void setNameList(List<Student> nameList) {
this.nameList = nameList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentService[ " +
"studentDao=" + studentDao +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", count=" + count +
", students1=" + students1 +
", nameList=" + nameList +
", students2=" + students2 +
", students3=" + students3 +
", studentMap=" + studentMap +
", properties=" + properties +
" ]";
}
}
准备测试方法
// 测试注入类型
@Test
public void t7(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
StudentService service = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(service);
}1. 注入bean类型
<!-- 注入bean类型 -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.example.dao.StudentDaoImpl1"/>
<!-- 写法1 -->
<bean id="studentService" class="com.example.service.StudentService">
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 写法2 -->
<!--<bean id="studentService" class="com.example.service.StudentService">
<property name="studentDao">
<ref bean="studentDao"/>
</property>
</bean>-->2. 注入基本数据类型
<!-- 注入基本数据类型 -->
<!-- 写法一 name:属性名 value:属性值 -->
<property name="name" value="程序员"/>
<!-- 写法二 name:属性名 value:属性值-->
<property name="count">
<value>10</value>
</property>3. 注入List集合
<!-- 注入List集合 -->
<!-- 简单的数据类型List集合 name:属性名 -->
<property name="students1" >
<list>
<value>上海</value>
<value>广州</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 对象类型的List集合 name:属性名 -->
<property name="nameList">
<list>
<bean class="com.example.pojo.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="几何心凉"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.example.pojo.Student">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="哈士奇"/>
<property name="address" value="上海"/>
</bean>
</list>
</property>4. 注入Set集合
<!-- 注入Set集合 -->
<property name="students2">
<set>
<value>深圳</value>
<value>北京</value>
</set>
</property>5. 注入Map集合
<!-- 注入Map集合 -->
<property name="students3">
<map>
<entry key="哈士奇" value="上海"/>
<entry key="几何心凉" value="北京"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- 注入对象类型map类型 -->
<property name="names2">
<map>
<entry key="student1" value-ref="s1"/>
<entry key="student2" value-ref="s2"/>
</map>
</property> <bean id="s1" class="com.example.pojo.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="几何心凉"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
<bean id="s2" class="com.example.pojo.Student">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="哈士奇"/>
<property name="address" value="上海"/>
</bean>6. 注入Properties对象
<!-- 注入properties -->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="配置1">值1</prop>
<prop key="配置2">值2</prop>
</props>
</property>运行测试方法测试一下

往期专栏&文章相关导读
1. Maven系列专栏文章
| Maven系列专栏 | Maven工程开发 |
| Maven聚合开发【实例详解---5555字】 |
2. Mybatis系列专栏文章
| Mybatis系列专栏 | MyBatis入门配置 |
| Mybatis入门案例【超详细】 | |
| MyBatis配置文件 —— 相关标签详解 | |
| Mybatis模糊查询——三种定义参数方法和聚合查询、主键回填 | |
| Mybatis动态SQL查询 --(附实战案例--8888个字--88质量分) | |
| Mybatis分页查询——四种传参方式 | |
| Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存(带测试方法) | |
| Mybatis分解式查询 | |
| Mybatis关联查询【附实战案例】 | |
| MyBatis注解开发---实现增删查改和动态SQL | |
| MyBatis注解开发---实现自定义映射关系和关联查询 |
3. Spring系列专栏文章
| Spring系列专栏 | Spring IOC 入门简介【自定义容器实例】 |
| IOC使用Spring实现附实例详解 | |
| Spring IOC之对象的创建方式、策略及销毁时机和生命周期且获取方式 | |
| Spring DI简介及依赖注入方式和依赖注入类型 | |
| Spring IOC相关注解运用——上篇 | |
| Spring IOC相关注解运用——下篇 | |
| Spring AOP简介及相关案例 | |
| 注解、原生Spring、SchemaBased三种方式实现AOP【附详细案例】 | |
| Spring事务简介及相关案例 | |
| Spring 事务管理方案和事务管理器及事务控制的API | |
| Spring 事务的相关配置、传播行为、隔离级别及注解配置声明式事务 |









