前言
本文主要介绍ES的常用请求,让大家能快速上手ES的使用
主要参考官网的Quick start指引。
一、请求方式
向Elasticsearch发送请求主要有2种方式:
1、使用rest api发送http请求,比如curl命令
curl -X GET -u elastic:123456 "localhost:9200/?pretty"
2、使用Kibana’s console的请求工具
进入kibana界面,打开控制台——》开发工具
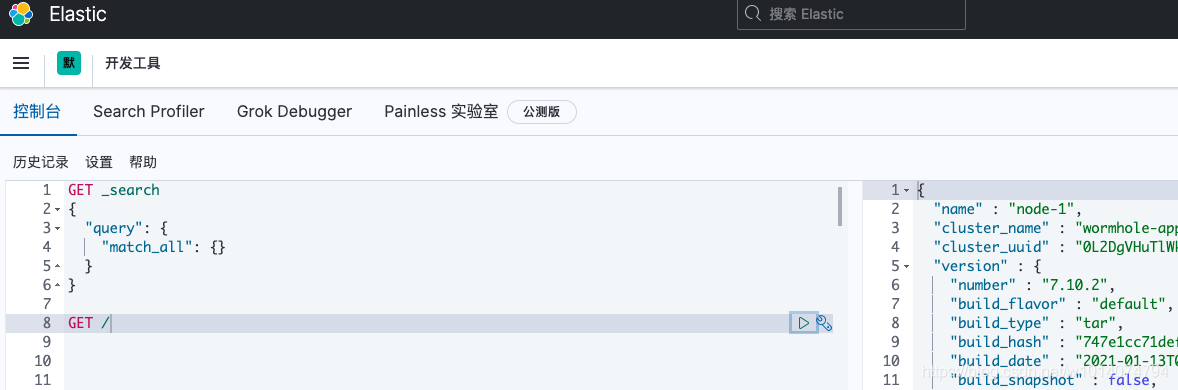
官网中的示例代码可以直接拷贝到Kibana中执行,也可以Copy as curl复制到服务器上执行curl请求。
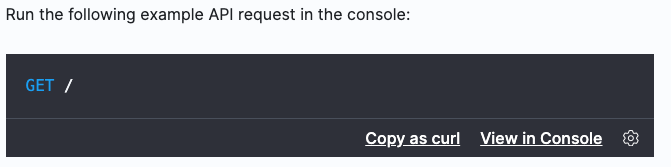
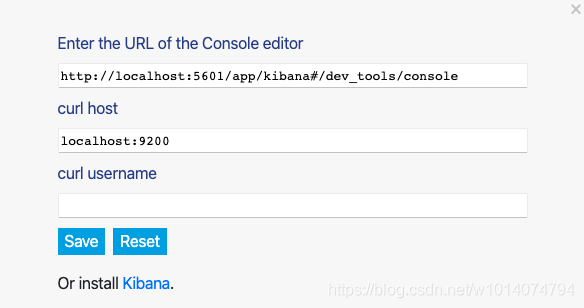
通过设置按钮,还可以配置对应的kibana控制台的相关信息。这样当点击View in Console就能直接跳转到
我们自己安装的kibana的控制台。
这里为了请求的方便和简洁性,下面的演示中都是采用Kibana’s console的请求工具向ES发送请求。
二、创建索引
创建索引时,注意一下三点:
1、设置索引的settings属性
2、设置索引的mappings属性
3、设置索引的别名
官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.13/indices-create-index.html
方式一:只创建索引
PUT my-index-000001
方式二:创建索引并同时指定settings、mappings、aliases
PUT my-index-000001
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": "4",
"number_of_replicas": "0",
"index": {
"refresh_interval": "30s"
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"@timestamp" : {
"type" : "date"
}
}
},
"aliases": {
"alias1": {}
}
}
说明:
采用PUT命令创建索引my-index-000001,并同时设置索引的settings和mappings。
settings主要用来配置索引的一些全局属性,比如分片数,副本数,刷新频次,等。示例中通过number_of_shards指定了索引的分片数为1。
mappings主要用来声明索引中包含的字段和类型,对应关系型数据库中的表结构声明。
三、设置setting
number_of_shards
说明:索引分片数量
索引分片数在索引创建好了之后就不能调整了,只能重建索引
number_of_replicas
说明:用来控制索引的副本数量
index.refresh_interval
说明:索引刷新频率
数据写入后几秒可以被搜索到,默认是 1s。每次索引的 refresh 会产生一个新的 lucene 段, 这会导致频繁的合并行为,如果业务需求对实时性要求没那么高,可以将此参数调大,实际调优告诉我,该参数确实很给力,cpu 使用率直线下降。
设置settings:
PUT /my-index-000001
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
}
}
也可以简写成:
PUT /my-index-000001
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
}
修改settings:
说明:修改索引的副本数目。
PUT my-index-000001/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas": "2"
}
查看索引的详情:
GET /my-index-000001/
查看索引的settings:
GET /my-index-000001/_settings
查看索引的mapping:
GET /my-index-000001/_mapping
注意⚠️:
分片数number_of_shards的属性在索引创建后就不能修改了。
四、设置mapping
说明:
映射是定义文档及其包含的字段如何存储和索引的过程。
每个文档都是字段的集合,每个字段都有自己的数据类型。 映射数据时,您创建一个映射定义,其中包含与文档相关的字段列表。 映射定义还包括元数据字段,例如 _source 字段,用于自定义处理文档相关元数据的方式。
mapping属性主要用来设置索引中的字段名称和字段类型以及text字段的分词策略。
官网对mapping的介绍:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.13/mapping.html
mapping主要有2种类型:
1、自动映射 Dynamic mapping
当 Elasticsearch 在文档中检测到新字段时,它默认动态地将该字段添加到类型映射中。
也就是添加数据时,发现新的字段会自动添加类型映射。
2、精确映射 Explicit mapping
由用户自己定义索引的映射,这种方式会更加精准。
注意⚠️:
ES的mapping可以新增字段,但是对于已经存在的字段,只能添加属性,不能修改字段的类型。
如果需要修改已经存在的字段的type类型,只能进行重建索引reindex。
ES的mapping并不是不能修改,只是不能对已经存在的字段类型进行修改。
获取索引的mapping信息
GET /my-index-000001/_mapping
获取索引中单个字段的mapping信息
GET /my-index-000001/_mapping/field/content
设置mapping信息
PUT /my-index-000001/_mapping
{
"dynamic": false,
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"@timestamp" : {
"type" : "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
}
}
}
或
PUT /my-index-000001
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": false,
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"@timestamp" : {
"type" : "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
}
}
}
}
说明:
给索引添加4个字段,content、name、age、@timestamp。
其中content类型为text,会进行分词匹配,设置分词器为ik_max_word,查询分词器为ik_smart。
如果时间字段需要指定多种格式,可以采用如下方式声明:
"create_time" : {
"type" : "date",
"format" : "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}dynamic 参数控制是否动态添加新字段,并接受以下参数:
- true
新字段被添加到映射中(默认)。 - runtime
新字段作为运行时字段添加到映射中。 这些字段未编入索引,并在查询时从 _source 加载。 - false
新字段将被忽略。 这些字段不会被索引或可搜索,但仍会出现在返回命中的 _source 字段中。 这些字段不会添加到映射中,必须显式添加新字段。 - strict
如果检测到新字段,则会抛出异常并拒绝文档。 新字段必须显式添加到映射中。
给索引增加一个新的字段映射:
PUT /my-index-000001/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
五、设置索引别名
官网介绍:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.13/indices-aliases.html
索引别名是用于引用一个或多个现有索引的辅助名称。
大多数 Elasticsearch API 接受索引别名来代替索引。
一个索引别名能关联多个索引。可以用索引别名来代替真实索引名称查询。
方式一:创建索引时指定别名
PUT /my-index-000001
{
"aliases": {
"alias_1": {}
}
}
方式二:给已经存在的索引新增索引别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "add" : { "index" : "my-index-000001", "alias" : "alias1" } }
]
}
移除索引别名:
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "remove" : { "index" : "my-index-000001", "alias" : "alias1" } }
]
}
重命名索引别名:
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "remove" : { "index" : "my-index-000001", "alias" : "alias1" } },
{ "add" : { "index" : "my-index-000001", "alias" : "alias2" } }
]
}
六、添加数据
1、单条添加
- 指定索引ID添加单条数据
PUT /my-index-000001/_doc/1
{"content": "小天今天在研究大数据", "name": "小天", "age": 25,"@timestamp": "2018-05-08 16:25:42"}
- 自动生成索引ID添加单条数据
POST my-index-000001/_doc
{"content": "小天尝试通过POST添加单条数据", "name": "小天", "age": 25,"@timestamp": "2018-05-08 16:25:42"}
POST /my-index-000001/_doc?op_type=create
{"content": "小天今天去钓鱼", "name": "小天", "age": 25,"@timestamp": "2018-05-08 16:25:42"}
2、批量添加
通过bulk命令实现批量添加数据,可以通过create属性指定id,如果不指定则自动生成索引ID。
PUT /my-index-000001/_bulk
{ "create": { } }
{"content": "小明同学觉得java是最好的编程语言", "name": "小明", "age": 20,"@timestamp": "2020-05-08 16:25:42"}
{ "create": { "_id": "20210602060517329146" }}
{"content": "小明同学今天学习编程5个小时", "name": "小明", "age": 20,"@timestamp": "2020-05-08 16:25:42"}
通过添加refresh,批量添加数据后,立刻刷新索引。保证大批量的添加数据后,索引立刻刷新,可以立刻被检索到。
PUT /my-index-000001/_bulk?refresh
{ "create": { } }
{"content": "路见不平,拔刀相助", "name": "小李", "age": 29,"@timestamp": "2019-05-08 16:25:42"}
七、关闭索引
POST /my-index-000001/_close?wait_for_active_shards=0
八、开启索引
POST /my-index-000001/_open
九、删除索引
删除索引及索引中的数据
DELETE /my-index-000001
根据id删除单条索引数据
DELETE /my-index-000001/_doc/20210602060517329146
根据查询结果删除数据:
POST /my-index-000001/_delete_by_query?pretty
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
十、基础查询
1、查询全部
无条件查询,如果返回数据量过多,会自动分页。
GET /my-index-000001/_search
等同于match_all
GET /my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
2、指定返回字段
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": { }
},
"fields": [
"@timestamp"
],
"_source": false,
"sort": [
{
"@timestamp": "desc"
}
]
}
说明:
有时候我们不希望返回索引中的全部字段,那么可以通过fields属性指定需要返回的字段。
这里注意,如果通过fields指定了需要返回的字段,最好同时将_source属性设置为false,否则仍会会返回_source。
2、term精确查询
查看年龄age为25岁的记录:
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"query":{
"term":{
"age":25
}
}
}
查询姓名为小龙的记录:
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"query":{
"term":{
"name" : "小龙"
}
}
}
3、match分词匹配查询
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"content" : "Java编程"
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.9542089,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "my-index-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "rYv3ZXoBD69AlULo3Bnk",
"_score" : 2.9542089,
"_source" : {
"content" : "小明同学觉得java是最好的编程语言",
"name" : "小明",
"age" : 20,
"@timestamp" : "2020-05-08 16:25:42"
}
},
{
"_index" : "my-index-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "20210602060517329146",
"_score" : 1.1599741,
"_source" : {
"content" : "小明同学今天学习编程5个小时",
"name" : "小明",
"age" : 20,
"@timestamp" : "2020-05-08 16:25:42"
}
}
]
}
}说明:
只有text类型的字段才能进行分词匹配。输入的关键字“Java编程”被分解成了 “JAVA”、“编程”后才去和content分词解析后的数据进行匹配。
4、分页
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"from":0,
"size":2,
"query": {
"match_all": { }
},
"sort": [
{
"@timestamp": "asc"
}
]
}
说明:
from和size是起到分页的作用。from指定起始记录行,size指定返回多少条数据。
5、排序
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": { }
},
"sort": [
{
"@timestamp": "desc"
}
]
}
说明:
通过sort属性指定排序字段,desc倒序,asc正序。
6、范围查询
GET /my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2020-01-08 16:25:42",
"lt": "2020-10-08 16:25:42"
}
}
},
"fields": [
"@timestamp"
],
"_source": false,
"sort": [
{
"@timestamp": "desc"
}
]
}
说明:
通过range实现范围查询。
范围操作符包含:
- gt : 大于
- gte : 大于等于
- lt : 小于
- lte : 小于等于
7、聚合查询
按年龄统计记录数
GET /my-index-000001/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my-agg-name": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
注意⚠️:
这类聚合统计一定要指定size为0
结果:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 8,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my-agg-name" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 25,
"doc_count" : 5
},
{
"key" : 20,
"doc_count" : 2
},
{
"key" : 29,
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
}
}
}总结
本文主要是参考官网的Quick start快速入门ES的实操指南,希望对大家快速上手ES有所帮助。










