Definition of Binary Search Tree:
1.Every node in the left subtree must be less than the current node
2.Every node in the right subtree must be greater than the current node
Here the tree in Figure 2 is a binary search tree.
Finding a data in a Binary Search Tree
Look at the simple queue below
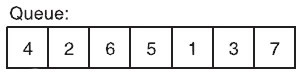
When we search a number in the queue, we need average (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7) / 7 = 4 comparisons to find the number.
When we put those numbers in a binary search tree, we only need average(1 + 2 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3) / 7 = 2.42 comparisons to find the number. The Binary Search Tree 's search algorithm is roughly O(log2n) However this is the best-case .
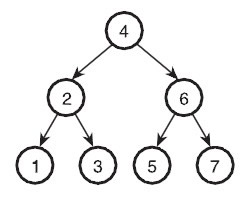
Figure 2
Delete Node in a Binary Search Tree
Because search and insert node in a Binary Search Tree is easy, So We skip it. Focus on how to delete node.
To delete node P, there are three possbilities,(1) P is just a leaf, (2) P only has one subtree, (3) P has two subtrees.
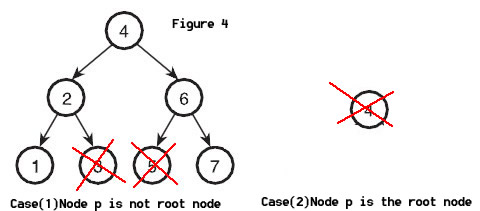
For Case (1), To delete 5 in Figure 4, just set its parent's left-child field to Zero, and delete the node P. To delete 3 in Figure 4, just set its parent's right-child field to Zero, and delete the node P. So We need to know node P is its parent's right child or left child. However, If Node p is tree's root nood, just delete the root nood.
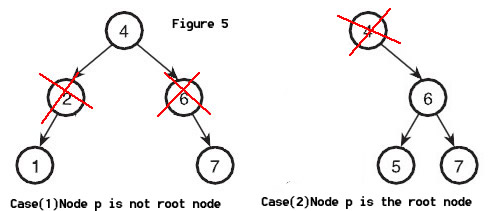
For Case(2), To delete 6 in Figure 5, We assume Node p have a parent node called PP, So we change PP's right child pointer to points P's only child. In the Figure 5, To delete 6, 4's right child became 7. To delete 2, 4's left child became 1. However, when the Node p is the root node, We set its only child to be the new root node.
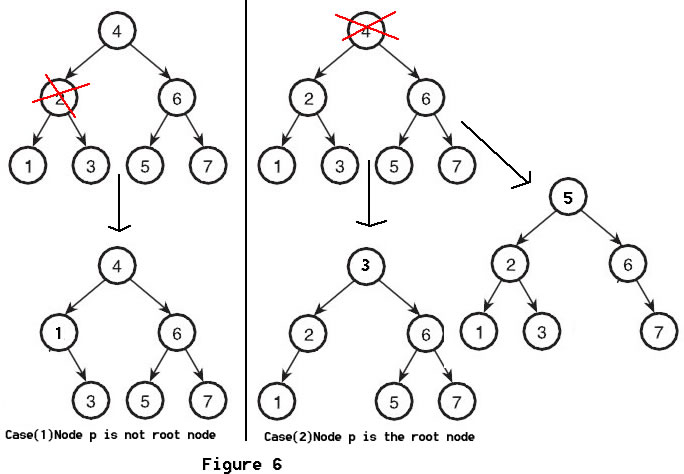
For Case(3). Look at case(2) in Figure 6, when We delete node 4, We replace this element with either the largest element in its left subtree or the smallest element in its right subtree. So it remains be a Binary Search Tree. In our code below, we replace the element with the largest element in its left subtree. When the node P is the root node like in the case(2) in Figure 6, we set new element to be the root node.
Customized Binary Search Tree Code
#ifndef _BSTREE_
#define _BSTREE_
template<class T> class BSTree;
template<class T>
class Node{
friend BSTree<T>;
public:
Node(){left = right = parent = 0;}
private:
T data;
Node<T>* left,* right, *parent;
};
template<class T>
class BSTree{
private:
Node<T>* root;
bool InsertWhenHaveRoot( const T& v, Node<T>* newNode );
void BeginToDelete( Node<T>* item );
public:
BSTree(){root = 0;}
~BSTree();
bool Search(const T& v);
bool Insert(const T& v);
bool Delete(const T& v);
void Clear();
};
template<class T>
BSTree<T>::~BSTree(){
while(root){
Delete(root->data);
}
};
template<class T>
bool BSTree<T>::Search(const T& v){
Node<T>* item = root;
while(item){
if(v > item->data){
item = item->right;
}else if(v < item->data){
item = item->left;
}else{ //when v == item->data, find the item
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
template<class T>
bool BSTree<T>::Insert(const T& v){
Node<T>* newNode = new Node<T>;
newNode->data = v;
if(!root){ //if the tree is empty, the new node become the root.
root = newNode;
return true;
}else{
return InsertWhenHaveRoot(v, newNode);
}
}
template<class T>
bool BSTree<T>::Delete(const T& v){
Node<T>* item = root;
while(item){
if(v > item->data){ //keep finding
item = item->right;
}else if(v < item->data){ //keep finding
item = item->left;
}else{ //begin to delete, because v == item->data
BeginToDelete(item);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
template<class T>
void BSTree<T>::Clear(){
while(root){
Delete(root->data);
}
}
template<class T>
bool BSTree<T>::InsertWhenHaveRoot( const T& v, Node<T>* newNode )
{
Node<T>* item = root;
while(item){
if(v > item->data){ //keep finding or insert the new node to the right
if(item->right){
item = item->right;
}else{
item->right = newNode;
newNode->parent = item;
return true;
}
}else if(v < item->data){//keep finding or insert the new node to the left
if(item->left){
item = item->left;
}else{
item->left = newNode;
newNode->parent = item;
return true;
}
}else{//have duplicate data,failure insert
return false;
}
}
}
template<class T>
void BSTree<T>::BeginToDelete( Node<T>* item )
{
if(item->left && item->right){// it both have right and left child
//find max item in its left children
Node<T>* searchNode = item->left;
while(searchNode->right){
searchNode = searchNode->right;
}
searchNode->right = item->right;
if(item->parent){
if(item->parent->right == item){
item->parent->right = searchNode;
}else{
item->parent->left = searchNode;
}
}else{
root = searchNode;
root->parent = 0;
}
delete item;
}else{
//it have no child or only have one child
Node<T>* c = new Node<T>;
if(item->right){
c = item->right;
}else{
c = item->left;
}
if(item == root){
root = c;
if(root)root->parent = 0;
}else{
if(item->parent->right == item){
item->parent->right = c;
}else{
item->parent->left = c;
}
}
delete item;
}
}
#endif
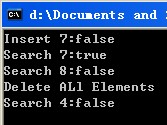
Simply Test the Binary Search Tree
// BSTree.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "BSTree1.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
BSTree<int> bsTree;
bsTree.Insert(4);
bsTree.Insert(3);
bsTree.Insert(6);
bsTree.Insert(5);
bsTree.Insert(7);
cout << "Insert 7:" << boolalpha << bsTree.Insert(7) << endl;
cout << "Search 7:" << boolalpha << bsTree.Search(7) << endl;
cout << "Search 8:" << boolalpha << bsTree.Search(8) << endl;
cout << "Delete ALl Elements" << endl;
bsTree.Clear();
cout << "Search 4:" << boolalpha << bsTree.Search(7) << endl;
int i;
cin >> i;
return 0;
}