目录
- 1 SQL语句的执行过程介绍
- 2 SQL执行的入口分析
- 2.1 为Mapper接口创建代理对象
- 2.2 执行代理逻辑
- 3 查询语句的执行过程分析
- 3.1 selectOne方法分析
- 3.2 sql获取
- 3.3 参数设置
- 3.4 SQL执行和结果集的封装
- 4 更新语句的执行过程分析
- 4.1 sqlsession增删改方法分析
- 4.2 sql获取
- 4.3 参数设置
- 4.4 SQL执行
- 5 小结
1 SQL语句的执行过程介绍
MyBatis核心执行组件: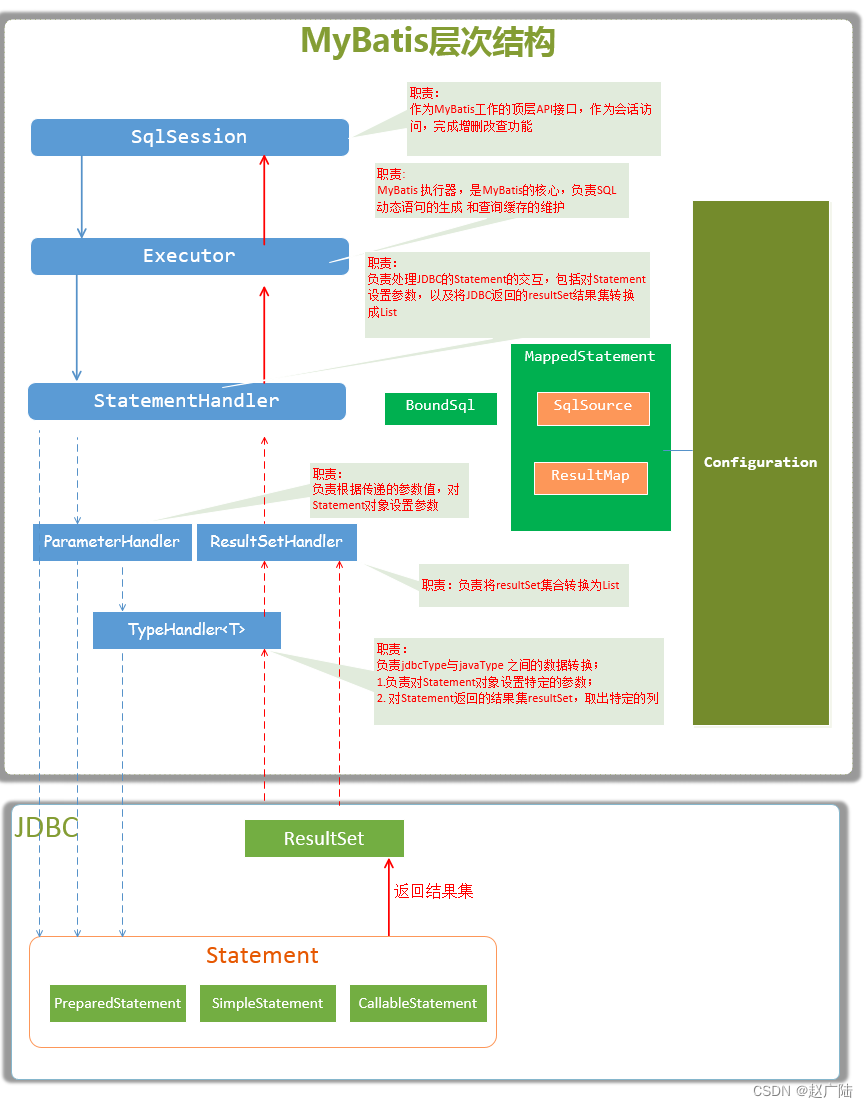
2 SQL执行的入口分析
2.1 为Mapper接口创建代理对象
// 方式1:
User user = session.selectOne("com.oldlu.dao.UserMapper.findUserById", 101);
// 方式2:
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.findAll();2.2 执行代理逻辑
方式1入口分析:
session是DefaultSqlSession类型的,因为sqlSessionFactory默认生成的SqlSession是
DefaultSqlSession类型。
selectOne()会调用selectList()。
// DefaultSqlSession类
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds
rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// CURD操作是交给Excetor去处理的
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds,
Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: "
+ e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}方式2入口分析:
获取代理对象:
//DefaultSqlSession类 ====================>
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
// Configuration类 ====================>
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
//MapperRegistry ----> apperProxyFactory.newInstance ====================>
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//从缓存中获取该Mapper接口的代理工厂对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>)
knownMappers.get(type);
//如果该Mapper接口没有注册过,则抛异常
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the
MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//【使用代理工厂创建Mapper接口的代理对象】
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e,
e);
}
}
//MapperProxyFactory --->此时生成代理对象 ====================>
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//Mybatis底层是调用JDK的Proxy类来创建代理实例
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new
Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession,
mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}代理对象执行逻辑:
//MapperProxy ====================>
/**代理对象执行的方法,代理以后,所有Mapper的方法调用时,都会调用这个invoke方法*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws
Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
//如果是Object方法,则调用方法本身
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
//调用接口方法:根据被调用接口的Method对象,从缓存中获取MapperMethodInvoker对象
//apper接口中的每一个方法都对应一个MapperMethodInvoker对象,而MapperMethodInvoker
对象里面的MapperMethod保存着对应的SQL信息和返回类型以完成SQL调用 ...
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
/**
获取缓存中MapperMethodInvoker,如果没有则创建一个,而MapperMethodInvoker内部封装这一
个MethodHandler
*/
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
//如果调用接口的是默认方法(default方法)
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new
DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new
DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException |
InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
//如果调用的普通方法(非default方法),则创建一个PlainMethodInvoker并放
入缓存,其中MapperMethod保存对应接口方法的SQL以及入参和出参的数据类型等信息
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface,
method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
// MapperProxy内部类: PainMethodInvoker ====================>
// 当cacheInvoker返回了PalinMethodInvoker实例之后,紧接着调用了这个实例的
PlainMethodInvoker:invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession
sqlSession) throws Throwable {
//Mybatis实现接口方法的核心: MapperMethod::execute方法:
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
// MapperMethod ====================>
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 将args进行解析,如果是多个参数则,则根据@Param注解指定名称将参数转换为Map,
如果是封装实体则不转换
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(),
param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(),
param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(),
param));
break;
}
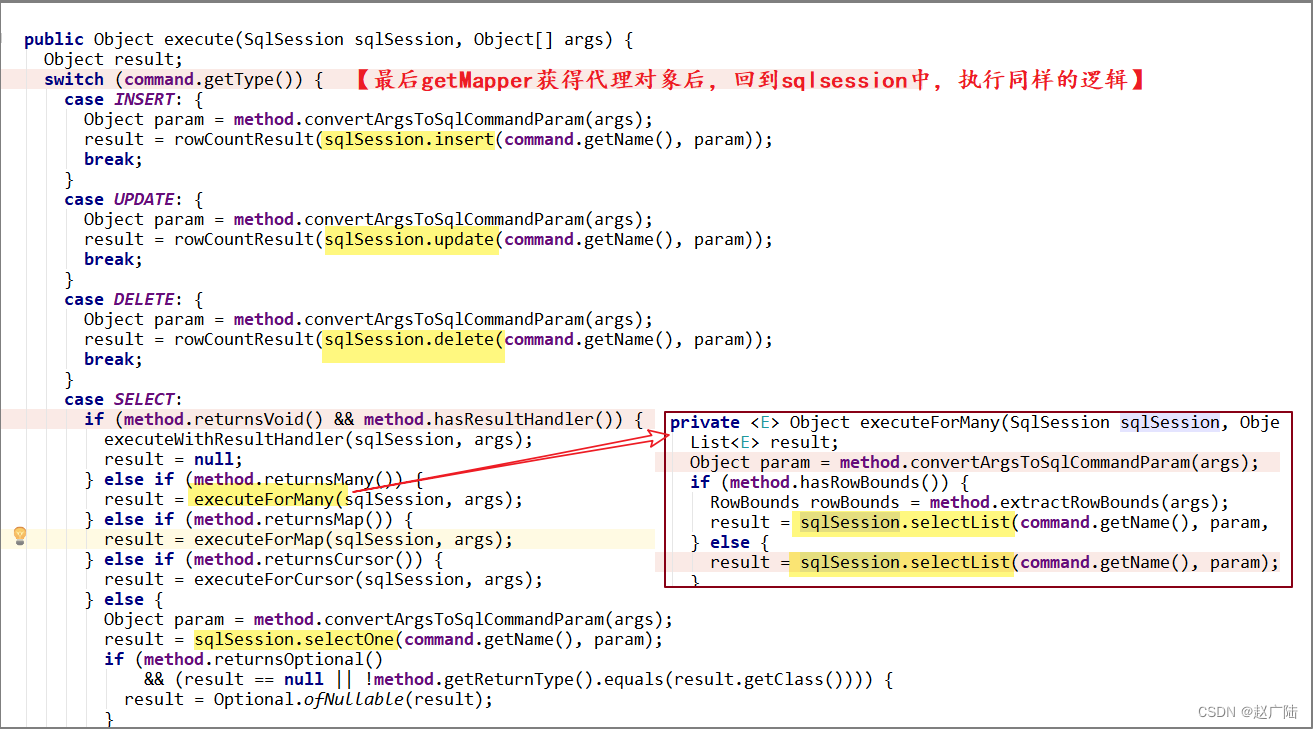
case SELECT:
//查询操作
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//解析参数,因为SqlSession::selectOne方法参数只能传入一个,但是我们
Mapper中可能传入多个参数,
//有可能是通过@Param注解指定参数名,所以这里需要将Mapper接口方法中的多个参
数转化为一个ParamMap,
//也就是说如果是传入的单个封装实体,那么直接返回出来;如果传入的是多个参数,
实际上都转换成了Map
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//可以看到动态代理最后还是使用SqlSession操作数据库的
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null ||
!method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " +
command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() &&
!method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method
with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
// 此时我们发现: 回到了sqlsession中
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// ...
return result;
}
3 查询语句的执行过程分析
3.1 selectOne方法分析
// DefaultSqlSession类 ===============>
// selectOne
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// //selectOne()会调用selectList()。
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be
returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
// selectList
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds
rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// CURD操作是交给Excetor去处理的
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds,
Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: "
+ e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}3.2 sql获取
// CachingExecutor ===============>
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds
rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取绑定的sql命令,比如"SELECT * FROM xxx"
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds
rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key,
boundSql);
}
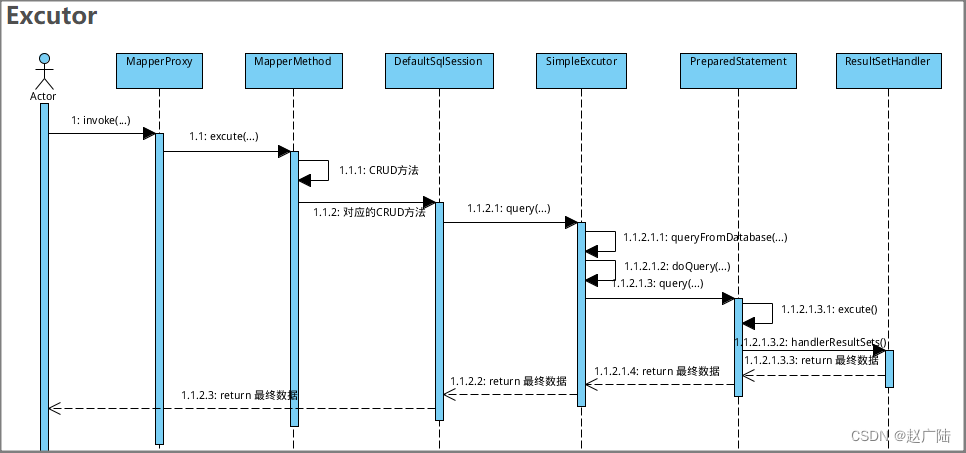
//真正执行query操作的是SimplyExecutor代理来完成的,SimplyExecutor的父类BaseExecutor的
query方法中:
// BaseExecutor类:SimplyExecutor的父类 =================>
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds
rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws
SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a
query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//localCache是一级缓存,如果找不到就调用queryFromDatabase从数据库中查找
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) :
null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler,
key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
//第一次,没有缓存,所以会调用queryFromDatabase方法来执行查询。
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(...) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
// SimpleExecutor类 ============================>
public <E> List<E> doQuery(...) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(....);
// 1:SQL查询参数的设置
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// StatementHandler封装了Statement
// 2:SQL查询操作和结果集的封装
return handler.<E>query(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}3.3 参数设置
// SimplyExecutor类 ============================>
// 【1】 参数设置: prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog)
throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 通过getConnection方法来获取一个Connection,
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 调用prepare方法来获取一个Statement
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置SQL查询中的参数值 ***
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
// DefaultParameterHandler ============================> 此时参数设置成功
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting
parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if
(typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject =
configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for
mapping.....");
}
}
}
}
}3.4 SQL执行和结果集的封装
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
return delegate.<E>query(statement);
}
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)
throws SQLException {
// 这里就到了熟悉的PreparedStatement了
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行SQL查询操作
ps.execute();
// 结果交给ResultHandler来处理
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
// DefaultResultSetHandler类(封装返回值,将查询结果封装成Object对象)
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling
results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping =
nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap =
configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
4 更新语句的执行过程分析
- Executor 的 update 方法分析
insert、update 和 delete 操作都会清空一二级缓存 - doUpdate 方法
- PreparedStatementHandler 的 update 方法
默认是创建PreparedStatementHandler,然后执行prepareStatement方法。
执行结果为受影响行数
执行更新语句的SQL
4.1 sqlsession增删改方法分析
// DefaultSqlSession ===============>
public int insert(...) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
public int update(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
public int delete(...) {
return update(....);
}
// insert 、delete操作是通过调用update语句进行的相关逻辑
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 增删改 最终底层都是 update
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " +
e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}4.2 sql获取
// CachingExecutor ===============>
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws
SQLException {
// 执行增删改,清除缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 跳转BaseExecutor
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
// BaseExecutor ===============>
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an
update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清除 LocalCache 一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
//执行 doUpdate
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
// SimpleExecutor ===============>
// doUpdate
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(...);
// 【1】.获取statement,并进行参数映射
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 【2】.handler.update()方法执行具体sql指令
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}4.3 参数设置
// SimplyExecutor类 ============================>
//【1】 prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog)
throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 使用connection对象信息创建statement,并将超时时间绑定
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// parameterize方法设置sql执行时候需要的参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
// DefaultParameterHandler ============================> 此时参数设置成功
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting
parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if
(typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject =
configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for
mapping.....");
}
}
}
}
}4.4 SQL执行
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
return delegate.update(statement);
}
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
// 这里就是底层JDBC的PreparedStatement 操作了
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行SQL增删改操作
ps.execute();
// 获取影响的行数
int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);
// 返回影响的行数
return rows;
}5 小结
mybatis执行SQL的流程都是:
1.根据statement字符串从configuration中获取对应的mappedStatement;
2.根据获取的mappedStatement创建相应的Statement实例;
3.根据传入的参数对statement实例进行参数设置;
4.执行statement并执行后置操作;










