系列文章目录
目录
654.最大二叉树
凡是涉及到构造二叉树的题目都要用前序遍历(中左右),先构造根节点然后才能递归去构造左右子树。与 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 和 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 相似。注意索引分割。
递归法
[左闭右开)
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, 0, nums.length);
}
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree1(int[] nums, int begin, int end) {
if (begin >= end) {
return null;
}
//中(找到根节点并构建节点)
int maxIndex = begin;//先初始最大节点为开始节点
int maxVal = nums[maxIndex];
for (int i = begin + 1; i < end; i++) {//从第二个节点开始在区间上遍历找最大节点
if (nums[i] > maxVal) {
maxVal = nums[i];
maxIndex = i;//最大值下标
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[maxIndex]);//构造节点
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, begin, maxIndex);//左
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, maxIndex + 1, end);//右
return root;
}
}
[左闭右闭]
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree1(int[] nums, int begin, int end) {
//终止条件
if (begin > end) {
return null;
}
//中
int maxIndex = begin;
int maxVal = nums[maxIndex];
for (int i = begin + 1; i <= end; i++) {
if (nums[i] > maxVal) {
maxIndex = i;
maxVal = nums[maxIndex];
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);//构造节点
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, begin, maxIndex - 1);
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, maxIndex + 1, end);
return root;
}
}
617.合并二叉树
同时遍历就同时判断两个树的情况,改变其中一棵树的结构来当做需要生成的新的数。
递归法(前中后序都可,以前序为例)
终止条件:如果其中一个二叉树的根节点为null,则不需要覆盖,直接用另一个二叉树返回就行。如果都是null,第一个if中root1 = null,会自动返回root2的null。
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
//终止条件
// 如果其中一个二叉树的根节点为null,则不需要覆盖,直接用另一个二叉树返回就行
// 如果都是null,第一个if中root1 = null,会自动返回root2的null
if (root1 == null) return root2;
if (root2 == null) return root1;
//重复利用一下t1这个树,t1就是合并之后树的根节点(就是修改了原来树的结构)。
root1.val = root1.val + root2.val; // 中
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left); //左
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right); //右
return root1;
}
}
迭代法(类似 101. 对称二叉树 写法,可用双端队列/单端队列<栈>,以单端队列为例)
通过队列成对存放两个树的节点即可。
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null) return root2;
if (root2 == null) return root1;
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.add(root1);
que.add(root2);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node1 = que.poll();
TreeNode node2 = que.poll();
node1.val = node1.val + node2.val;
if (node1.left != null && node2.left != null) {
que.add(node1.left);
que.add(node2.left);
} else if (node2.left != null) {
node1.left = node2.left;
}
if (node1.right != null && node2.right != null){
que.add(node1.right);
que.add(node2.right);
}else if(node2.right != null){
node1.right = node2.right;
}
}
return root1;
}
}
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
①递归法(没有涉及到前中后序,因为二叉树的顺序性已经帮我们确定了我们的遍历顺序)
递归三部曲:
-
确定递归函数的参数和返回值:递归函数的参数传入的就是根节点和要搜索的数值,返回的就是以这个搜索数值所在的节点。
-
确定终止条件:如果
root为空,或者找到这个数值了,就返回root节点。
-
确定单层递归的逻辑:
TreeNode result = null;初始化递归返回结果,默认值为null。- 如果当前节点的
val大于目标val,证明val只可能出现在当前节点的左子树中,返回左子树的搜索结果result。 - 如果当前节点的
val小于目标val,证明val只可能出现在当前节点的右子树中,返回右子树的搜索结果result。
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
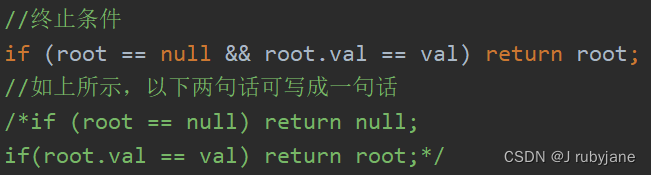
//终止条件
if (root == null || root.val == val) return root;
//如上所示,以下两句话可写成一句话
/*if (root == null) return null;
if(root.val == val) return root;*/
//其实这个也可以不写,如果不写不影响结果,但就会让递归多进行了一层。
/*if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val != val) return null*/
TreeNode result = null;//递归返回结果,默认值为null
if (root.val > val) {
result = searchBST(root.left, val);//向左搜索
}
if (root.val < val) {
result = searchBST(root.right, val);//向右搜索
}
return result;//如果左右都搜索不到,则返回null。
}
}
②迭代法
普通二叉树迭代
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null||root.val==val) return root;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
//if(node!=null){
if(node.val==val)return node;
if(node.left!=null)stack.push(node.left);//空节点不入栈
if(node.right!=null)stack.push(node.right);
//}
}
return null;
}
}
利用二叉搜索树特点,自己使用了栈/队列(麻烦多此一举)
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null || root.val == val) return root;
TreeNode node = null;
que.add(root);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
node = que.poll();
if (node == null || node.val == val) break;
if (node.val > val) {
que.add(node.left);
}
if (node.val < val) {
que.add(node.right);
}
}
return node;
}
}
利用二叉搜索树特点,优化,可以不需要栈
注:向左向右遍历时必须使用 else if,因如果满足代码中的①,则 root 值已经改变,如果直接使用 if,则会用改变的root值(假设为null)去判断是否成立,此时会报空指针异常!
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.val == val) return root;
if (root.val > val) root = root.left;//①
else if (root.val < val) root = root.right;
//此处 必须使用 else if,因如果满足①,则 root 值已经改变,
// 如果直接使用 if,则会用改变的root值(假设为null)去判断是否成立,
// 此时会报空指针异常!
/* if (root.val > val) root = root.left;
else if (root.val < val) root = root.right;
else return root;*/
}
return null;
}
}
98.验证二叉搜索树
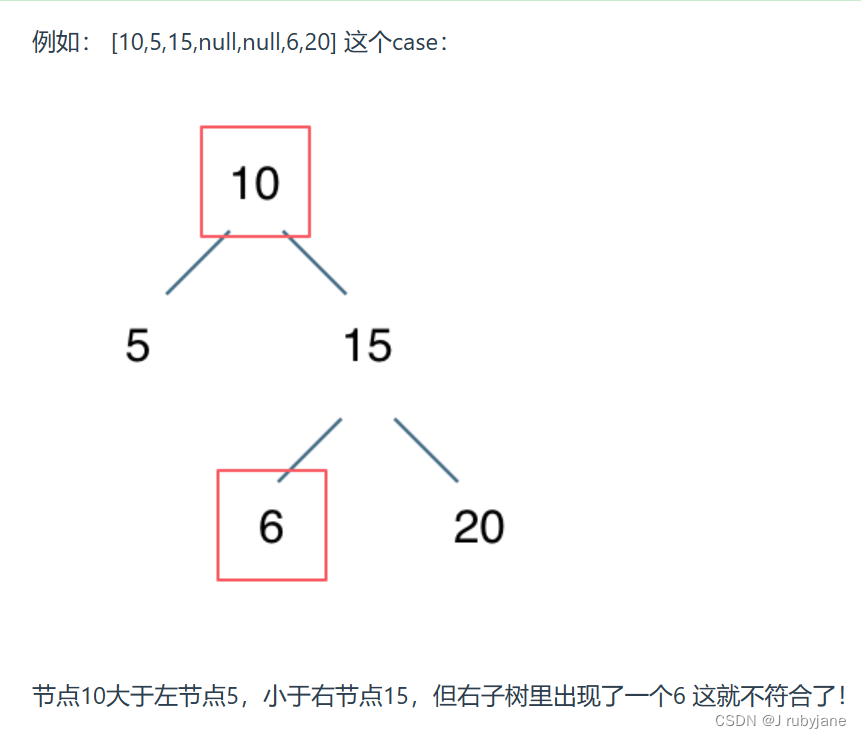
这道题目比较容易陷入两个陷阱:
-
陷阱1:不能单纯的比较左节点小于中间节点,右节点大于中间节点就完事了。
if (root.val > root.left.val && root.val < root.right.val) { return true; } else { return false; }我们要比较的是 左子树所有节点小于中间节点,右子树所有节点大于中间节点。所以以上代码的判断逻辑是错误的。
-
陷阱2


如②中方法所示。
①暴力解法 有效的二叉搜索树的中序遍历数组为升序数组(递归+for循环)
(1)递归,中序遍历,存放所有节点的val;判断中序遍历数组是否是升序数组。
(2)注:二叉搜索树中不能有重复元素。故数组前后元素不能=,要严格<才是升序。
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Solution {
List<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
// 递归,中序遍历,存放所有节点的val
inorder(root);
// 判断数组是否保持升序,至少有一个节点,如果只有一个节点,则不进入for循环
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size() - 1; i++) {
if (nodes.get(i) >= nodes.get(i + 1)) return false;// 注意:不能等于,要严格小于才是升序
}
return true;
}
// 递归,中序遍历,存放所有节点的val
public void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
//boolean result=false;
isValidBST(root.left);//左
nodes.add(root.val);
isValidBST(root.right);//右
}
}
②递归法 中序遍历二叉树过程中检测是否升序
class Solution {
TreeNode max;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
// 左
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if (!left) return false;
// 中
if (max != null && max.val >= root.val) return false;
max = root;
// 右
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return right;
}
}
③迭代法(中序遍历)
统一迭代
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root == null) return true;
stack.push(root);
TreeNode max = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
if (node != null) {
stack.pop();
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);//右
}
stack.push(node);//中
stack.push(null);
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);//左
}
} else {//中节点处理逻辑
stack.pop();
TreeNode preNode = stack.pop();
if (max != null && max.val >= preNode.val) return false;
max = preNode;
}
}
return true;
}
}
普通迭代(借助指针访问节点,栈处理元素)
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
if (root == null) return true;
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode max = null;
while (cur != null || !st.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
st.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;//左
} else {
TreeNode node = st.pop();
if (max != null && max.val >= node.val) return false;//中
max = node;
cur = node.right;//右
}
}
return true;
}
}










