引⼊相关依赖 35
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.god.ibatis</groupId>
<artifactId>course7</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<!--依赖-->
<dependencies>
<!--dom4j依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--jaxen依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<!-- 编译代码使用的jdk版本-->
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<!-- 运行程序使用的jdk版本-->
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
</project>
1. 第一步创建基础类 35
代码在org.god.ibatis.utils
Resources类这个工具类专门完成“类路径”中资源的加载。
package org.god.ibatis.utils;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* godbatis框架提供的一个工具类。 35
* 这个工具类专门完成“类路径”中资源的加载。
*/
public class Resources {
/**
* 工具类的构造方法都是建议私有化的。
* 因为工具类中的方法都是静态的,不需要创建对象就能调用。
* 为了避免new对象,所有构造方法私有化。
* 这只是一种编程习惯。
*/
private Resources(){}
/**
* 从类路径当中加载资源。
* @param resource 放在类路径当中的资源文件。
* @return 指向资源文件的一个输入流。
*/
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource){
return ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(resource);
}
}2. 第二步分析SqlSessionFactory类该有的属性 36
2.1 MappedStatement 36
普通的java类。POJO,封装了一个SQL标签。 36
一个MappedStatement对象对应一个SQL标签。
一个SQL标签中的所有信息封装到MappedStatement对象当中。

代码在org.god.ibatis.core
MappedStatement
package org.god.ibatis.core;
/**
* 普通的java类。POJO,封装了一个SQL标签。 36
* 一个MappedStatement对象对应一个SQL标签。
* 一个SQL标签中的所有信息封装到MappedStatement对象当中。
* 面向对象编程思想。
*/
public class MappedStatement {
/**
* sql语句
*/
private String sql;
/**
* 要封装的结果集类型。有的时候resultType是null。
* 比如:insert delete update语句的时候resultType是null。
* 只有当sql语句是select语句的时候resultType才有值。
*/
private String resultType;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MappedStatement{" +
"sql='" + sql + '\'' +
", resultType='" + resultType + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
public String getResultType() {
return resultType;
}
public void setResultType(String resultType) {
this.resultType = resultType;
}
public MappedStatement(String sql, String resultType) {
this.sql = sql;
this.resultType = resultType;
}
public MappedStatement() {
}
}2.1 分析SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类 35-36
提供⼀个⽆参数构造⽅法,再提供⼀个build⽅法,该build⽅法要返回SqlSessionFactory对象
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.Node;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.god.ibatis.utils.Resources;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* SqlSessionFactory构建器对象。
* 通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法来解析
* godbatis-config.xml文件,然后创建SqlSessionFactory对象。
*/
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
/**
* 无参数构造方法。
*/
public SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(){}
/**
* 解析godbatis-config.xml文件,来构建SqlSessionFactory对象。
* @param in 指向godbatis-config.xml文件的一个输入流。
* @return SqlSessionFactory对象。
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream in){
SqlSessionFactory factory = null;
try {
// 解析godbatis-config.xml文件
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(in);
Element environments = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("/configuration/environments");
String defaultId = environments.attributeValue("default");
Element environment = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("/configuration/environments/environment[@id='" + defaultId + "']");
Element transactionElt = environment.element("transactionManager");
Element dataSourceElt = environment.element("dataSource");
List<String> sqlMapperXMLPathList = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取整个配置文件中所有的mapper标签
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//mapper");
nodes.forEach(node -> {
Element mapper = (Element) node;
String resource = mapper.attributeValue("resource");
sqlMapperXMLPathList.add(resource);
});
// 获取数据源对象
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource(dataSourceElt);
// 获取事务管理器
Transaction transaction = getTransaction(transactionElt,dataSource);
// 获取mappedStatements
Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = getMappedStatements(sqlMapperXMLPathList);
// 解析完成之后,构建SqlSessionFactory对象。
factory = new SqlSessionFactory(transaction, mappedStatements);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return factory;
}
/**
* 解析所有的SqlMapper.xml文件,然后构建Map集合。 43
* @param sqlMapperXMLPathList
* @return
*/
private Map<String, MappedStatement> getMappedStatements(List<String> sqlMapperXMLPathList) {
Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new HashMap<>();
sqlMapperXMLPathList.forEach(sqlMapperXMLPath -> {
try {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(Resources.getResourceAsStream(sqlMapperXMLPath));
Element mapper = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("mapper");
String namespace = mapper.attributeValue("namespace");
List<Element> elements = mapper.elements();
elements.forEach(element -> {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
// 这里进行了namespace和id的拼接,生成最终的sqlId
String sqlId = namespace + "." + id;
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
String sql = element.getTextTrim();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement(sql, resultType);
mappedStatements.put(sqlId, mappedStatement);
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
return mappedStatements;
}
/**
* 获取事务管理器的 42
* @param transactionElt 事务管理器标签元素
* @param dataSource 数据源对象
* @return
*/
private Transaction getTransaction(Element transactionElt, DataSource dataSource) {
Transaction transaction = null;
String type = transactionElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase();
if (Const.JDBC_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) {
transaction = new JdbcTransaction(dataSource, false); // 默认是开启事务的,将来需要手动提交的。
}
if (Const.MANAGED_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) {
transaction = new ManagedTransaction();
}
return transaction;
}
/**
* 获取数据源对象 41
* @param dataSourceElt 数据源标签元素
* @return
*/
private DataSource getDataSource(Element dataSourceElt) {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
// 获取所有的property
List<Element> propertyElts = dataSourceElt.elements("property");
propertyElts.forEach(propertyElt -> {
String name = propertyElt.attributeValue("name");
String value = propertyElt.attributeValue("value");
map.put(name, value);
});
DataSource dataSource = null;
String type = dataSourceElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase();
if (Const.UN_POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) {
dataSource = new UnPooledDataSource(map.get("driver"), map.get("url"), map.get("username"), map.get("password"));
}
if (Const.POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) {
dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
}
if (Const.JNDI_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) {
dataSource = new JNDIDataSource();
}
return dataSource;
}
}
2.2 分析SqlSessionFactory 类 36-37
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 37
SqlSessionFactory
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* SqlSessionFactory对象: 35
* 一个数据库对应一个SqlSessionFactory对象。
* 通过SqlSessionFactory对象可以获取SqlSession对象。(开启会话)
* 一个SqlSessionFactory对象可以开启多个SqlSession会话。
*/
public class SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 事务管理器属性 37
* 事务管理器是可以灵活切换的。
* SqlSessionFactory类中的事务管理器应该是面向接口编程的。
* SqlSessionFactory类中应该有一个事务管理器接口。
*/
private Transaction transaction;
/**
* 存放sql语句的Map集合。 36
* key是sqlId
* value是对应的SQL标签信息对象。
*/
private Map mappedStatements;
public Transaction getTransaction() {
return transaction;
}
public void setTransaction(Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
}
public Map getMappedStatements() {
return mappedStatements;
}
public void setMappedStatements(Map mappedStatements) {
this.mappedStatements = mappedStatements;
}
/**
* 获取Sql会话对象。 45
* @return
*/
public SqlSession openSession(){
// 开启会话的前提是开启连接。(连接打开了)
transaction.openConnection();
// 创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = new SqlSession(this);
return sqlSession;
}
public SqlSessionFactory(Transaction transaction, Map mappedStatements) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.mappedStatements = mappedStatements;
}
public SqlSessionFactory() {
}
}3. 第三步抽取事务管理器的接口 37
3.1 Transation事务管理器接口。
事务管理器接口。
所有的事务管理器都应该遵循该规范。
JDBC事务管理器,MANAGED事务管理器都应该实现这个接口。
Transaction事务管理器:提供管理事务方法。
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 37,40
Transaction
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.sql.Connection;
/**
* 事务管理器接口。 37
* 所有的事务管理器都应该遵循该规范。
* JDBC事务管理器,MANAGED事务管理器都应该实现这个接口。
* Transaction事务管理器:提供管理事务方法。
*/
public interface Transaction {
/**
* 提交事务
*/
void commit();
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
void rollback();
/**
* 关闭事务
*/
void close();
/**
* 真正的开启数据库连接。
*/
void openConnection();
/**
* 获取数据库连接对象的。
*/
Connection getConnection();
}4. 第四步事务管理器的实现 38
4.1 分析JdbcTransaction类实现Transation接口 38
代码在org.god.ibatis.core
JdbcTransaction
4.2 ManagedTransaction类实现Transation接口 38
代码在org.god.ibatis.core
ManagedTransaction
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.sql.Connection;
/**
* MANAGED事务管理器。(godbatis对这个类就不再实现了。) 38
*/
public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction{
@Override
public void commit() {
}
@Override
public void rollback() {
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
@Override
public void openConnection() {
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
return null;
}
}5. 第五步数据源的实现 39
5.1 UnPooledDataSource实现类 39
代码在org.god.ibatis.core
UnPooledDataSource
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* 数据源的实现类:UNPOOLED (重点实现这种方式。) 38
* 不使用连接池,每一次都新建Connection对象。
*/
public class UnPooledDataSource implements javax.sql.DataSource{
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
/**
* 创建一个数据源对象。
* @param driver
* @param url
* @param username
* @param password
*/
public UnPooledDataSource(String driver, String url, String username, String password) {
try {
// 直接注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
this.url = url;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
return connection;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}5.2 PooledDataSource实现类 39
代码在org.god.ibatis.core
PooledDataSource
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* 数据源的实现类:POOLED 38
* 使用godbatis框架内置的数据库连接池来获取Connection对象。(这个不实现了。)
*/
public class PooledDataSource implements javax.sql.DataSource{
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 从数据库连接池当中获取Connection对象。(这个数据库连接池是我godbatis框架内部封装好的。)
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}5.3 JNDIDataSource实现类 39
代码在org.god.ibatis.core
JNDIDataSource
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* 数据源的实现类:JNDI 38
* 使用第三方的数据库连接池获取Connection对象。(这个不实现了。)
*/
public class JNDIDataSource implements javax.sql.DataSource{
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}6. 第六步事务管理器改造 40
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 40
JdbcTransaction
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* JDBC事务管理器(godbatis框架目前只对JdbcTransaction进行实现。) 38
*/
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction{
/**
* 数据源属性
* 经典的设计:面向接口编程。
*/
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* 自动提交标志
* true表示自动提交
* false表示不采用自动提交
*/
private boolean autoCommit;
/**
* 连接对象
*/
private Connection connection;
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
return connection;
}
/**
* 创建事务管理器对象
* @param dataSource
* @param autoCommit
*/
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource dataSource, boolean autoCommit) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
@Override
public void commit() {
try {
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback() {
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void openConnection(){
if (connection == null) {
try {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
// 开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}7. 第七步获取数据源对象 41
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 41
是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder里面的方法getDataSource
/**
* 获取数据源对象
* @param dataSourceElt 数据源标签元素
* @return
*/
private DataSource getDataSource(Element dataSourceElt) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
// 获取所有的property
List propertyElts = dataSourceElt.elements("property");
propertyElts.forEach(propertyElt -> {
String name = propertyElt.attributeValue("name");
String value = propertyElt.attributeValue("value");
map.put(name, value);
});
DataSource dataSource = null;
String type = dataSourceElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase();
if (Const.UN_POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) {
dataSource = new UnPooledDataSource(map.get("driver"), map.get("url"), map.get("username"), map.get("password"));
}
if (Const.POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) {
dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
}
if (Const.JNDI_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) {
dataSource = new JNDIDataSource();
}
return dataSource;
}8. 第八步获取事务管理器对象 42
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 42
是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder里面的方法getTransaction
**
* 获取事务管理器的
* @param transactionElt 事务管理器标签元素
* @param dataSource 数据源对象
* @return
*/
private Transaction getTransaction(Element transactionElt, DataSource dataSource) {
Transaction transaction = null;
String type = transactionElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase();
if (Const.JDBC_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) {
transaction = new JdbcTransaction(dataSource, false); // 默认是开启事务的,将来需要手动提交的。
}
if (Const.MANAGED_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) {
transaction = new ManagedTransaction();
}
return transaction;
}9. 第九步获取存储的SQLMap集合 43
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 43
是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder里面的方法getMappedStatements
/**
* 解析所有的SqlMapper.xml文件,然后构建Map集合。
* @param sqlMapperXMLPathList
* @return
*/
private Map getMappedStatements(List sqlMapperXMLPathList) {
Map mappedStatements = new HashMap<>();
sqlMapperXMLPathList.forEach(sqlMapperXMLPath -> {
try {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(Resources.getResourceAsStream(sqlMapperXMLPath));
Element mapper = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("mapper");
String namespace = mapper.attributeValue("namespace");
List elements = mapper.elements();
elements.forEach(element -> {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
// 这里进行了namespace和id的拼接,生成最终的sqlId
String sqlId = namespace + "." + id;
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
String sql = element.getTextTrim();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement(sql, resultType);
mappedStatements.put(sqlId, mappedStatement);
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
return mappedStatements;
}10. 第十步测试框架 44
代码在org.god.ibatis.test 44
是GodBatisTest里的方法testSqlSessionFactory
@Test
public void testSqlSessionFactory(){
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("godbatis-config.xml"));
System.out.println(sqlSessionFactory);
}11. 第十一 十二 十三 步 45-47
封装SqlSession对象 45
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 46-47
SqlSession
package org.god.ibatis.core;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 专门负责执行SQL语句的会话对象 45
*/
public class SqlSession {
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
public SqlSession(SqlSessionFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
/**
* 执行insert语句,向数据库表当中插入记录。 46
* @param sqlId sql语句的id
* @param pojo 插入的数据。
* @return
*/
public int insert(String sqlId, Object pojo){
int count = 0;
try {
// JDBC代码,执行insert语句,完成插入操作。
Connection connection = factory.getTransaction().getConnection();
// insert into t_user values(#{id},#{name},#{age})
String godbatisSql = factory.getMappedStatements().get(sqlId).getSql();
// insert into t_user(id,name,age) values(?,?,?)
String sql = godbatisSql.replaceAll("#\\{[a-zA-Z0-9_$]*}", "?");
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给?占位符传值 47
// 难度是什么:
// 第一:你不知道有多少个?
// 第二:你不知道该将pojo对象中的哪个属性赋值给哪个 ?
// ps.String(第几个问号, 传什么值); // 这里都是setString,所以数据库表中的字段类型要求都是varchar才行。这是godbatis比较失败的地方。
int fromIndex = 0;
int index = 1;
while(true){
int jingIndex = godbatisSql.indexOf("#", fromIndex);
if (jingIndex < 0) {
break;
}
int youKuoHaoIndex = godbatisSql.indexOf("}", fromIndex);
String propertyName = godbatisSql.substring(jingIndex + 2, youKuoHaoIndex).trim();
fromIndex = youKuoHaoIndex + 1;
// 有属性名id,怎么获取id的属性值呢?调用getId()方法
//拼方法名
String getMethodName = "get" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1);
//利用反射机制根据方法名得到方法对象
Method getMethod = pojo.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(getMethodName);
//利用反射机制根据调用得到的方法从而获得属性值
Object propertyValue = getMethod.invoke(pojo);
//给?赋值
ps.setString(index, propertyValue.toString());
index++;
}
// 执行SQL语句
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return count;
}
/**
* 执行查询语句,返回一个对象。该方法只适合返回一条记录的sql语句。 49
* @param sqlId
* @param param
* @return
*/
public Object selectOne(String sqlId, Object param){
Object obj = null;
try {
Connection connection = factory.getTransaction().getConnection();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = factory.getMappedStatements().get(sqlId);
// 这是那个DQL查询语句
// select * from t_user where id = #{id}
String godbatisSql = mappedStatement.getSql();
String sql = godbatisSql.replaceAll("#\\{[a-zA-Z0-9_$]*}", "?");
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给占位符传值
ps.setString(1, param.toString());
// 查询返回结果集
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 要封装的结果类型。
String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType(); // org.god.ibatis.pojo.User
// 从结果集中取数据,封装java对象
if (rs.next()) {
//利用反射
// 获取resultType的Class
Class resultTypeClass = Class.forName(resultType);
// 调用无参数构造方法创建对象
obj = resultTypeClass.newInstance(); // Object obj = new User();
// 给User类的id,name,age属性赋值
// 给obj对象的哪个属性赋哪个值。 50
/*
mysql> select * from t_user where id = '1111';
+------+----------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------+------+
| 1111 | zhangsan | 20 |
+------+----------+------+
解决问题的关键:将查询结果的列名作为属性名。
列名是id,那么属性名就是:id
列名是name,那么属性名就是:name
*/
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
//getColumnName获取列名
String propertyName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
// 拼接方法名
String setMethodName = "set" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1);
// 获取set方法对象
Method setMethod = resultTypeClass.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, String.class);
// 调用set方法给对象obj属性赋值
setMethod.invoke(obj, rs.getString(propertyName));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
// 局部测试 47
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sql = "insert into t_user values(#{id},#{name},#{age})";
int fromIndex = 0;
int index = 1;
while(true){
int jingIndex = sql.indexOf("#", fromIndex);
if (jingIndex < 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(index);
index++;
int youKuoHaoIndex = sql.indexOf("}", fromIndex);
String propertyName = sql.substring(jingIndex + 2, youKuoHaoIndex).trim();
System.out.println(propertyName);
fromIndex = youKuoHaoIndex + 1;
}
}
/**
* 提交事务 46
*/
public void commit(){
factory.getTransaction().commit();
}
/**
* 回滚事务 46
*/
public void rollback(){
factory.getTransaction().rollback();
}
/**
* 关闭事务 46
*/
public void close(){
factory.getTransaction().close();
}
}insert方法实现 46 动态给占位符传值 47
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 46-47
是SqlSession类里面的insert
/**
* 执行insert语句,向数据库表当中插入记录。 46
* @param sqlId sql语句的id
* @param pojo 插入的数据。
* @return
*/
public int insert(String sqlId, Object pojo){
int count = 0;
try {
// JDBC代码,执行insert语句,完成插入操作。
Connection connection = factory.getTransaction().getConnection();
// insert into t_user values(#{id},#{name},#{age})
String godbatisSql = factory.getMappedStatements().get(sqlId).getSql();
// insert into t_user(id,name,age) values(?,?,?)
String sql = godbatisSql.replaceAll("#\\{[a-zA-Z0-9_$]*}", "?");
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给?占位符传值 47
// 难度是什么:
// 第一:你不知道有多少个?
// 第二:你不知道该将pojo对象中的哪个属性赋值给哪个 ?
// ps.String(第几个问号, 传什么值); // 这里都是setString,所以数据库表中的字段类型要求都是varchar才行。这是godbatis比较失败的地方。
int fromIndex = 0;
int index = 1;
while(true){
int jingIndex = godbatisSql.indexOf("#", fromIndex);
if (jingIndex < 0) {
break;
}
int youKuoHaoIndex = godbatisSql.indexOf("}", fromIndex);
String propertyName = godbatisSql.substring(jingIndex + 2, youKuoHaoIndex).trim();
fromIndex = youKuoHaoIndex + 1;
// 有属性名id,怎么获取id的属性值呢?调用getId()方法
//拼方法名
String getMethodName = "get" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1);
//利用反射机制根据方法名得到方法
Method getMethod = pojo.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(getMethodName);
//利用反射机制根据调用得到的方法从而获得属性值
Object propertyValue = getMethod.invoke(pojo);
//给?赋值
ps.setString(index, propertyValue.toString());
index++;
}
// 执行SQL语句
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return count;
}局部测试
代码在org.god.ibatis.core 47
是SqlSession里面的main
// 局部测试 47
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sql = "insert into t_user values(#{id},#{name},#{age})";
int fromIndex = 0;
int index = 1;
while(true){
int jingIndex = sql.indexOf("#", fromIndex);
if (jingIndex < 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(index);
index++;
int youKuoHaoIndex = sql.indexOf("}", fromIndex);
String propertyName = sql.substring(jingIndex + 2, youKuoHaoIndex).trim();
System.out.println(propertyName);
fromIndex = youKuoHaoIndex + 1;
}
}12. 第十四步测试插入数据 48
代码在org.god.ibatis.test 48
是GodBatisTest里的方法testInsertUser
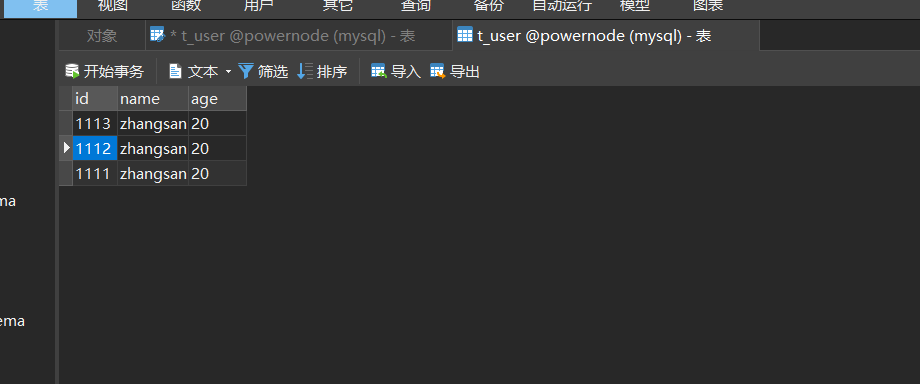
//测试插入数据 48
@Test
public void testInsertUser(){
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("godbatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 执行SQL insert
User user = new User("1111", "zhangsan", "20");
int count = sqlSession.insert("user.insertUser", user);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
13. 第十五步 selectOne方法的实现 49-50
代码在org.god.ibatis.test 49-50
是GodBatisTest里的方法selectOne
/**
* 执行查询语句,返回一个对象。该方法只适合返回一条记录的sql语句。 49
* @param sqlId
* @param param
* @return
*/
public Object selectOne(String sqlId, Object param){
Object obj = null;
try {
Connection connection = factory.getTransaction().getConnection();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = factory.getMappedStatements().get(sqlId);
// 这是那个DQL查询语句
// select * from t_user where id = #{id}
String godbatisSql = mappedStatement.getSql();
String sql = godbatisSql.replaceAll("#\\{[a-zA-Z0-9_$]*}", "?");
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给占位符传值
ps.setString(1, param.toString());
// 查询返回结果集
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 要封装的结果类型。
String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType(); // org.god.ibatis.pojo.User
// 从结果集中取数据,封装java对象
if (rs.next()) {
//利用反射
// 获取resultType的Class
Class resultTypeClass = Class.forName(resultType);
// 调用无参数构造方法创建对象
obj = resultTypeClass.newInstance(); // Object obj = new User();
// 给User类的id,name,age属性赋值
// 给obj对象的哪个属性赋哪个值。 50
/*
mysql> select * from t_user where id = '1111';
+------+----------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------+------+
| 1111 | zhangsan | 20 |
+------+----------+------+
解决问题的关键:将查询结果的列名作为属性名。
列名是id,那么属性名就是:id
列名是name,那么属性名就是:name
*/
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
//getColumnName获取列名
String propertyName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
// 拼接方法名
String setMethodName = "set" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1);
// 获取set方法对象
Method setMethod = resultTypeClass.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, String.class);
// 调用set方法给对象obj属性赋值
setMethod.invoke(obj, rs.getString(propertyName));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}14. 第十七步最终版测试 51
代码在org.god.ibatis.test 51
是GodBatisTest里的方法testSelectOne
//测试查询一条数据 51
@Test
public void testSelectOne(){
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("godbatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 执行SQL语句
Object obj = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectById", "1111");
System.out.println(obj);
sqlSession.close();
}