1.包含头文件#include<thread>
2.调用thread类创建一个对象
void print() {
cout << "子线程运行。。。。" << endl;
}
int main() {
thread test1(print);
cout << "主线程。。。。" << endl;
return 0;
}线程不做处理会调用abort函数终止线程
3.join函数,加入汇合线程,阻塞主线程,等待子线程执行结束才会回到主线程中
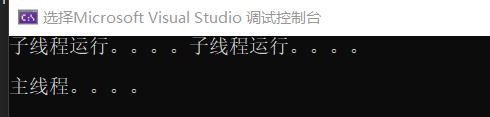
多个子线程是并行,
void print() {
Sleep(2000);
cout << "子线程运行。。。。" << endl;
}
int main() {
thread test1(print);
thread test2(print);
test2.join();
test1.join();
cout << "主线程。。。。" << endl;
return 0;
}
4.detach函数,打破依赖关系,主线程运行主线程的,子线程运行子线程的,把子线程驻留后台
void print() {
Sleep(2000);
cout << "子线程运行。。。。" << endl;
}
int main() {
thread test2(print);
test2.detach();
cout << "主线程。。。。" << endl;
return 0;
}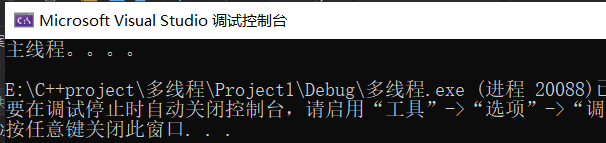
将看不到子线程的执行,因为主线程已经结束了
创建线程的方法
1.普通函数方式
2.通过类和对象
3.lambda表达式
4.带参的方式
5.带智能指针的方式
6.通过类的成员函数
智能指针
#include<memory>
void print(unique_ptr up){
cout<<"11111111"<<endl;
}
unique_ptr<string> p(new string("1111111"));
thread t1(print,std::move(p));unique_ptr是独占式指针,无法被拷贝所以必须使用move才能被子线程使用,一旦执行到代码末尾时,主线程中的(unique_ptr) p的地址已被置空,因为该地址已经move给了子线程中的up指针。
用成员函数指针做线程函数
class test1 {
public:
void thread_work(int num) {
cout << "111111111" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
test1 classobj;
thread throbj(&test1::thread_work, classobj, 15);
return 0;
}第一个参数为,类成员函数的地址,第二个参数为实例化的类对象,第三个参数才是函数需要的参数。
class test1 {
public:
void thread_work(int num) {
cout << "111111111" << endl;
}
void create_thread() {
thread throbj(&test1::thread_work, this, 15);
}
};








