
开启分布式事务
在之前的例子中,不管何种模式,我们只需要使用一个@GlobalTransaction注解就能开启事务,所以我们今天把扒一扒这个注解在背后到底做了哪些工作?
seata的设计基于二阶段提交协议,整体上可以分为三个大模块,即TM,RM,TC
TC (Transaction Coordinator) - 事务协调者
维护全局和分支事务的状态,驱动全局事务提交或回滚。
TM (Transaction Manager) - 事务管理器
定义全局事务的范围:开始全局事务、提交或回滚全局事务。
RM (Resource Manager) - 资源管理器
管理分支事务处理的资源,与TC交谈以注册分支事务和报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务提交或回滚。
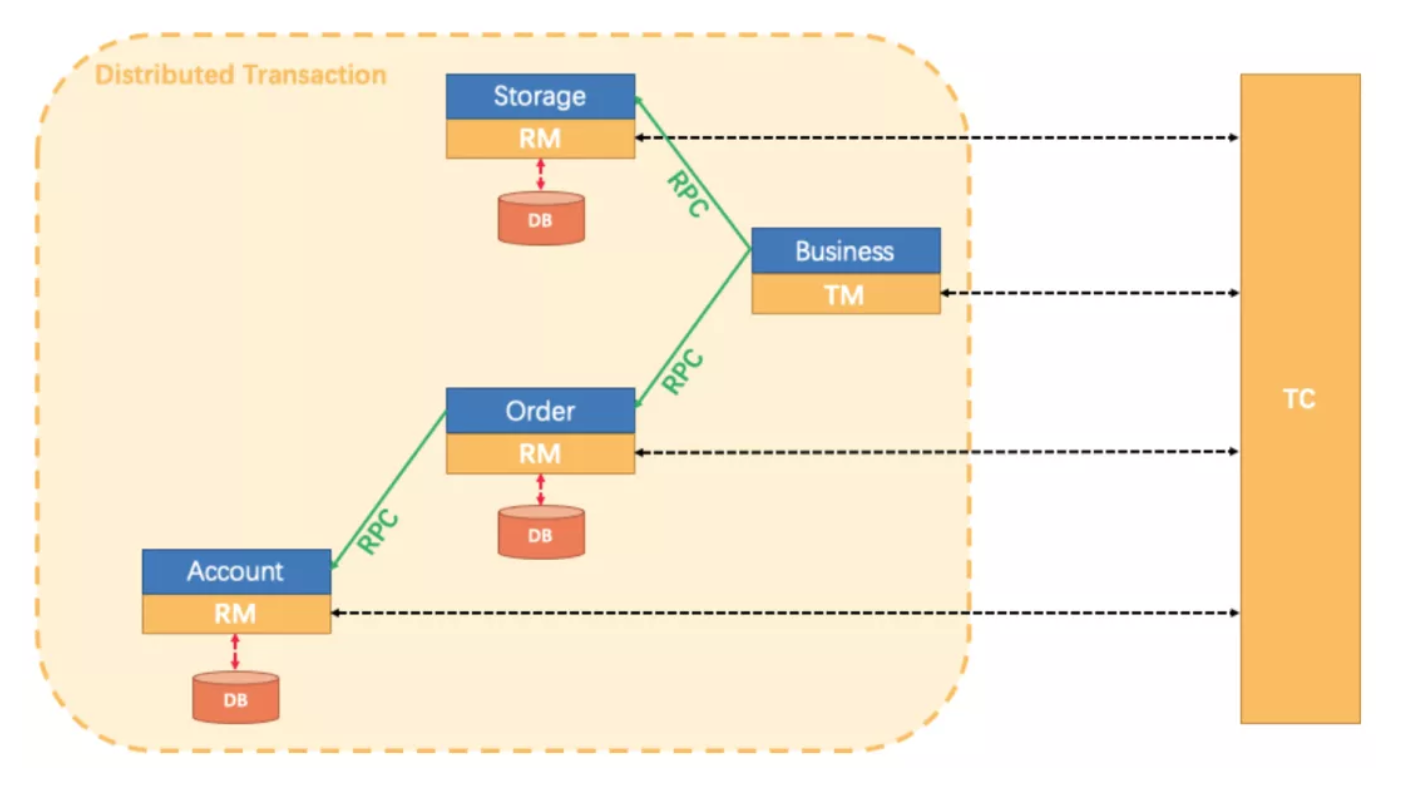
在seata中分布式事务的执行过程如下
- TM向TC申请开启一个全局事务,TC创建一个全局事务,并返回XID。XID在微服务调用链路的上下文传递
- RM向TC注册分支事务,分支事务的XID为上下文传递过来的XID。因此我们可以通过XID获取到全局事务和分支事务
- TM向TC发起针对XID的全局提交或者全局回滚请求
- TC调度XID下管辖的分支事务完成提交或回滚请求
源码分析
在分析开始,我们先来猜一下为什么一个@GlobalTransactional注解就能开启分布式事务
估计你也能猜到肯定是对增加了@GlobalTransactional注解的方法进行了代理,那这个方法是什么时候被代理的呢?代理的逻辑又是啥?
对方法进行代理是通过GlobalTransactionScanner类实现的(前文我们说过使用seata-spring-boot-starter的时候会往容器中注入这个类哈)
public class GlobalTransactionScanner extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator
implements ConfigurationChangeListener, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean

GlobalTransactionScanner重写了Spring Bean生命周期的3个阶段
- Bean初始化阶段:初始化TM RM客户端,建立与TC的长连接
- Bean初始化后阶段:给加了@GlobalTransactional,@GlobalLock,@TwoPhaseBusinessAction注解的方法生成代理类
- Bean销毁阶段:当Bean被销毁的时候关闭TM RM客户端
生成代理类
GlobalTransactionScanner重写了AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary方法,这个方法是用来自动生成代理类的
// GlobalTransactionScanner
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
// 已经处理过就不在处理
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
//check TCC proxy
// 是否是tcc模式的代理
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
//TCC interceptor, proxy bean of sofa:reference/dubbo:reference, and LocalTCC
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)interceptor);
} else {
Class<?> serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class<?>[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
// 目标类或者目标接口上不存在 @GlobalTransactional 或者 @GlobalLock
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
LOGGER.info("Bean[{}] with name [{}] would use interceptor [{}]", bean.getClass().getName(), beanName, interceptor.getClass().getName());
// 如果是普通的bean,走父类的方法生成代理类即可
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
// 如果已经是代理类,获取到advisor后,添加到该集合即可
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
// 根据上面的interceptor生成advisor
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, avr);
}
}
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
可以看到就是根据方法上的注解来选择不同的Advice生成代理对象
- 当方法被@TwoPhaseBusinessAction修饰时,相应的Advice为TccActionInterceptor
- 当方法被@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock修饰时,相应的Advice为GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
本节我们先看GlobalTransactionalInterceptor的增强逻辑,TccActionInterceptor的增强逻辑我们放到TCC那一节来分析
GlobalTransactionalInterceptor增强逻辑
前面我们已经介绍过GlobalTransactionalInterceptor是一个Advice,所以当执行被@GlobalTransactional注解或者@GlobalLock注解修饰的方式时,会执行到GlobalTransactionalInterceptor#invoke方法,我们来看一下这个方法做了哪些增强逻辑
// GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
// 执行代理逻辑
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
// 如果有@GlobalTransactional注解
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, globalTransactionalAnnotation);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
// 如果有@GlobalLock注解
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
当方法被@GlobalTransactional注解修饰时,会执行handleGlobalTransaction方法
当方法被@GlobalLock注解修饰时,会执行handleGlobalLock方法,我们分别来看这2个流程
方法被@GlobalTransactional修饰
执行TransactionalTemplate#handleGlobalTransaction方法,传入的参数为TransactionalExecutor的实现类,可以看到这个是一个匿名实现类
// TransactionalTemplate
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final GlobalTransactional globalTrxAnno) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
return transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
// 执行被代理的方法
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
public String name() {
String name = globalTrxAnno.name();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
/**
* 获取事务信息
*/
@Override
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
// reset the value of timeout
int timeout = globalTrxAnno.timeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);
transactionInfo.setName(name());
transactionInfo.setPropagation(globalTrxAnno.propagation());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInternal(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryInternal());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryTimes());
Set<RollbackRule> rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
TransactionalExecutor.Code code = e.getCode();
switch (code) {
case RollbackDone:
throw e.getOriginalException();
case BeginFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onBeginFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case CommitFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onCommitFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case RollbackFailure:
failureHandler.onRollbackFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
case RollbackRetrying:
failureHandler.onRollbackRetrying(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
default:
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("Unknown TransactionalExecutor.Code: %s", code));
}
} finally {
if (degradeCheck) {
EVENT_BUS.post(new DegradeCheckEvent(succeed));
}
}
}
TransactionalTemplate看类名就是一个模版方法,从中可以看到开始全局事务,回滚全局事务,提交全局事务的代码。
// TransactionalTemplate
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. Get transactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// 获取当前全局事务
// 如果不为空,则当前是事务参与者的角色
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
// 获取事务传播行为
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,
// else continue and execute with new transaction.
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
// 以事务发起者的角色开启一个新事务
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
// 开始事务
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.
// 回滚事务
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
// 提交事务
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}
- 获取当前事务上下文(有可能一个执行链路中有多个方法被@GlobalTransaction修饰)
- 然后是对事务传播行为的支持,可以看到和Spring中定义的事务传播行为差不多
- 如果当前事务上下文为空,则创建一个
- 接着就可以看到事务提交的模版方法,开始事务,执行业务逻辑,提交事务,或者回滚事务
需要注意的是,seata判断全局事务回滚和提交的依据是执行业务方法是否发生异常,如果发生异常则回滚,如果没有则不回滚。所以RM端当需要全局异常回滚时要抛出相应的异常,不然会导致回滚失败
方法被@GlobalLock修饰
@GlobalLock这个注解有什么用呢?
@GlobalLock只是用在seata at模式下的,当RM执行单独的本地事务,有可能会造成全局事务回滚失败,此时可以在相应的方法上加上@GlobalLock注解,让RM在本地事务提交前也需要获取全局锁,这样就不会造成全局事务回滚失败,更细节的知识我们在后续会分析。
Object handleGlobalLock(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final GlobalLock globalLockAnno) throws Throwable {
return globalLockTemplate.execute(new GlobalLockExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public GlobalLockConfig getGlobalLockConfig() {
GlobalLockConfig config = new GlobalLockConfig();
config.setLockRetryInternal(globalLockAnno.lockRetryInternal());
config.setLockRetryTimes(globalLockAnno.lockRetryTimes());
return config;
}
});
}
GlobalLockTemplate的执行逻辑比较简单
- 在RootContext中设置锁标志位,后续执行sql的时候会根据锁标志位来决定是否对sql进行代理(有锁标志位,或者事务为at模式才会对sql进行代理)
- 将获取全局锁的配置设置到线程上下文中
public class GlobalLockTemplate {
public Object execute(GlobalLockExecutor executor) throws Throwable {
boolean alreadyInGlobalLock = RootContext.requireGlobalLock();
if (!alreadyInGlobalLock) {
// 其实就是在RootContext设置一个标志位
RootContext.bindGlobalLockFlag();
}
// set my config to config holder so that it can be access in further execution
// for example, LockRetryController can access it with config holder
// @@GlobalTransactional 注解有可能会嵌套
// 所以先把上一个配置拿出来,替换成当前的,当方法执行完,再把原来的放回去
GlobalLockConfig myConfig = executor.getGlobalLockConfig();
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = GlobalLockConfigHolder.setAndReturnPrevious(myConfig);
try {
// 执行被代理的方法
return executor.execute();
} finally {
// only unbind when this is the root caller.
// otherwise, the outer caller would lose global lock flag
if (!alreadyInGlobalLock) {
RootContext.unbindGlobalLockFlag();
}
// if previous config is not null, we need to set it back
// so that the outer logic can still use their config
if (previousConfig != null) {
GlobalLockConfigHolder.setAndReturnPrevious(previousConfig);
} else {
GlobalLockConfigHolder.remove();
}
}
}
}
DefaultTransactionManager
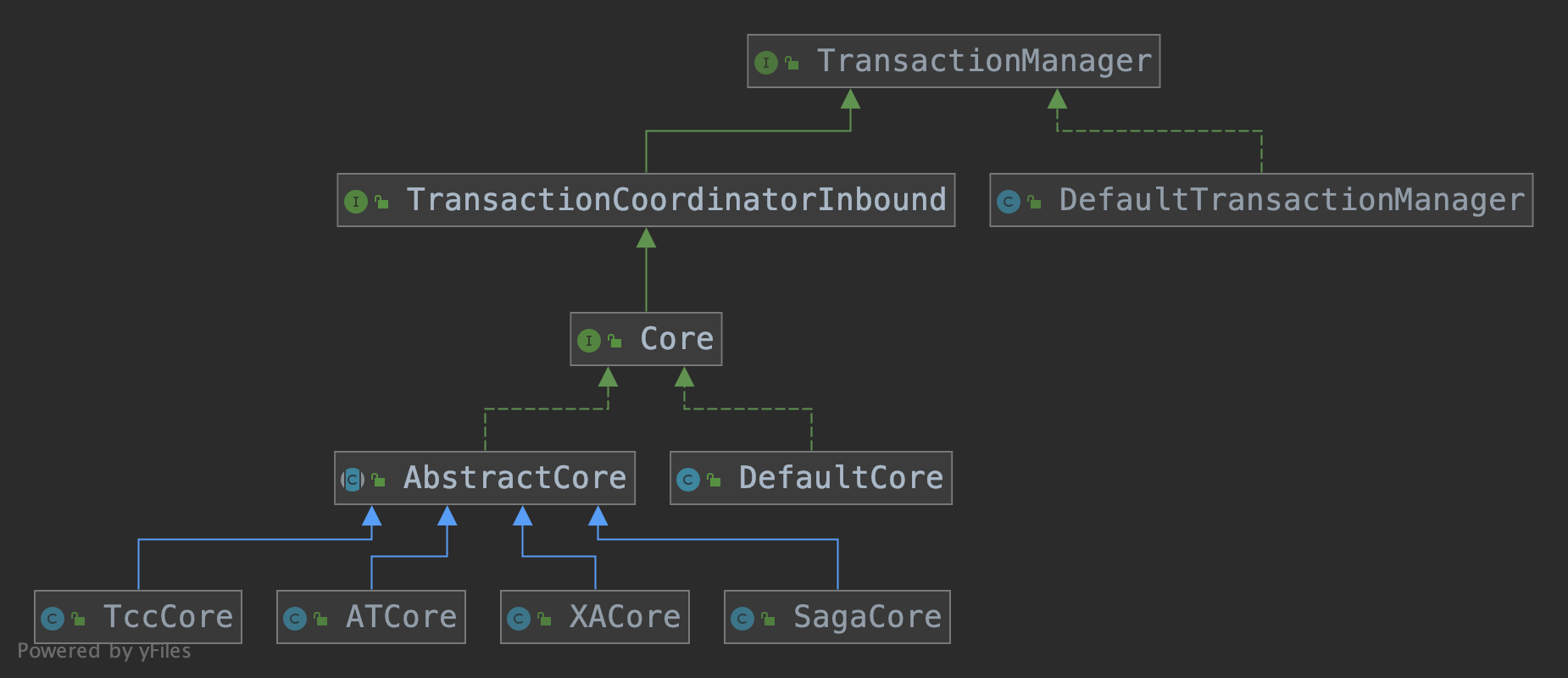
全局事务的开启,提交,回滚操作在TM端的操作都是由类DefaultTransactionManager来完成的,当然只是向TC端发送相应的请求
public class DefaultTransactionManager implements TransactionManager {
// 全局事务开启只是TM端单纯向TC端获取一个xid
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
return response.getXid();
}
@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
GlobalCommitRequest globalCommit = new GlobalCommitRequest();
globalCommit.setXid(xid);
GlobalCommitResponse response = (GlobalCommitResponse) syncCall(globalCommit);
return response.getGlobalStatus();
}
// 省略部分代码
}
而TC端也有事务管理器(Core及其实现类),它通过向分支事务发送最终的提交或回滚操作来完成全局事务的提交
参考博客










