基于PyTorch实现seq2seq模型来实现中文向英文的翻译。
Seq2Seq模型
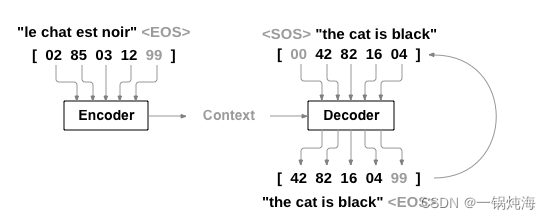
seq2seq模型主要由Encoder和Decoder这两部分组成,因为是序列到序列网络,之间有两个递归神经网络一起工作,将一个序列转换成另一个序列。编码器网络将输入序列压缩成向量,解码器将其展开为新序列。
我们的数据集是来自 http://www.manythings.org/anki/
![]()
找到这个将其下载下来。
1.文本预处理:
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
#做个标签 以上两个分别代表一个序列的开始和结束
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
# 形如 {"hello" : 3}
self.word2index = {}
# 统计每一个单词出现的次数
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
# 统计训练集出现的单词数
self.n_words = 2 # SOS 和 EOS已经存在了
def addSentence(self, sentence):
# 第一行为 Go. Va !
# 前面是英语,后面是中文,中间用tab分隔
for word in sentence.split(" "):
self.addWord(word)
def addWord(self, word):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
# 用现有的总词数作为新的单词的索引
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
# 将Unicode字符串转换为纯ASCII, 感谢https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
def unicodeToAscii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# 小写,修剪和删除非字母字符
def normalizeString(s):
# 转码之后变小写切除两边空白
s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip())
# 匹配.!?,并在前面加空格
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
# 将非字母和.!?的全部变为空白
#s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
print("Reading lines...")
# 读取文件并分为几行
# 每一对句子最后会有个换行符\n
# lines ==> ['Go.\tVa !', 'Run!\tCours\u202f!'...]
lines = open(r"填写自己数据集保存的相对位置的地址",
encoding="utf-8").read().strip().split("\n")
# 将每一行拆分成对并进行标准化
# pairs ==> [["go .","va !"],...]
pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split("\t")] for l in lines]
pairs = np.delete(pairs, 2, axis=1) #这里 你打开数据集你发现每一行是这样一个格式
English + TAB + The Other Language + TAB + Attribution 我们做的是把pairs的第三个对(Attribution)去掉,(TAB是空格),我们留下的是 [English] 和[The Other Language] 这两个相对的语言对
# 反向对,实例Lang
# 源文件是先英语后中文
# 换完之后就是先中后英
reverse 反转输入数据,这是seq2seq在深度学习进阶这本书中 提到改进的两个点之一,反转之后学习进展会更快,最终进度也提高,如果不反转,正确率会下降很多 有兴趣可以自己做个实验
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(lang2)
output_lang = Lang(lang1)
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1)
output_lang = Lang(lang2)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
lang1 = "cmn"
lang2 = "eng"
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2)
print("input_lang:", input_lang)
print("output_lang:", output_lang)
print("pairs中的前五个:", pairs[:5])
把pairs打印出来看看 现在我们看出它已经是我们所需要的数据对了。
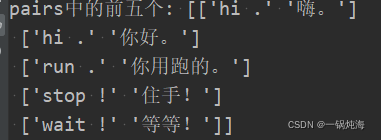
可以对比原来的数据集,把每句话最后一句话去掉了。
最终代码:
from __future__ import unicode_literals, print_function, division
from io import open
import unicodedata
import re
import random
import os
import os
import numpy as np
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
# 形如 {"hello" : 3}
self.word2index = {}
# 统计每一个单词出现的次数
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
# 统计训练集出现的单词数
self.n_words = 2 # SOS 和 EOS已经存在了
def addSentence(self, sentence):
# 第一行为 Go. Va !
# 前面是英语,后面是法语,中间用tab分隔
for word in sentence.split(" "):
self.addWord(word)
def addWord(self, word):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
# 用现有的总词数作为新的单词的索引
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
# 将Unicode字符串转换为纯ASCII, 感谢https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
def unicodeToAscii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# 小写,修剪和删除非字母字符
def normalizeString(s):
# 转码之后变小写切除两边空白
s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip())
# 匹配.!?,并在前面加空格
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
# 将非字母和.!?的全部变为空白
#s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
print("Reading lines...")
# 读取文件并分为几行
# 每一对句子最后会有个换行符\n
# lines ==> ['Go.\tVa !', 'Run!\tCours\u202f!'...]
lines = open(r"绝对路径",
encoding="utf-8").read().strip().split("\n")
# 将每一行拆分成对并进行标准化
# pairs ==> [["go .","va !"],...]
pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split("\t")] for l in lines]
pairs = np.delete(pairs, 2, axis=1)
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(lang2)
output_lang = Lang(lang1)
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1)
output_lang = Lang(lang2)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
lang1 = "cmn"
lang2 = "fra"
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2)
print("input_lang:", input_lang)
print("output_lang:", output_lang)
print("pairs中的前五个:", pairs[:5])
MAX_LENGTH = 10
eng_prefixes = (
"i am ", "i m ",
"he is", "he s ",
"she is", "she s ",
"you are", "you re ",
"we are", "we re ",
"they are", "they re "
)
def filterPair(p):
return len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes)
# 留下符合条件的
def filterPairs(pairs):
return [pair for pair in pairs if filterPair(pair)]
def prepareData(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse)
print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
pairs = filterPairs(pairs)
print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
print("Counting words...")
for pair in pairs:
input_lang.addSentence(pair[0])
output_lang.addSentence(pair[1])
print("Counted words:")
print(input_lang.name, input_lang.n_words)
print(output_lang.name, output_lang.n_words)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepareData('eng', 'cmn', True)
# 随机输出pair对
print(random.choice(pairs))
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
# 调用父类初始化方法
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
# 初始化必须的变量
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
# gru的输入为三维,两个参数均指的是最后一维的大小
# tensor([1,1,hidden_size])
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
# embedded.size() ==> tensor([1,1,hidden_size])
# -1的好处是机器会自动计算
# 这里用view扩维的原因是gru必须接受三维的输入
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
output = embedded
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
# 初始化隐层状态全为0
# hidden ==> tensor([1,1,hidden_size])
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size):
super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
# input_features ==> hidden_size
# output_features ==> output_size
self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
# Log(Softmax(X))
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
output = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
# output.size() ==> [1,1,hidden_size]
# output的第一个1是我们用以适合gru输入扩充的
# 所以用output[0]选取前面的
output = self.softmax(self.out(output[0]))
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.dropout_p = dropout_p
self.max_length = max_length
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size)
# 因为会将prev_hidden和embedded在最后一个维度
# 即hidden_size,进行拼接,所以要*2
# max_length用以统一不同长度的句子分配的注意力
# 最大长度句子使用所有注意力权重,较短只用前几个
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2,
self.max_length) # 输入一个大小为hidden-size*2长度的【batch-size,hidden-size*2]向量 输出为【batch-size,max_length]
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length)
self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p)
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs):
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
embedded = self.dropout(embedded)
# 因为第一维只是适应模型输入扩充的
# 所以拼接时,只需要取后面两个维度
attn_weights = F.softmax(
self.attn(torch.cat((embedded[0], hidden[0]), 1)), dim=1)
# bmm ==> batch matrix multiplication
# e.g. a.size() ==> tensor([1,2,3])
# b.size() ==> tensor([1,3,4])
# torch.bmm(a,b).size() ==> tensor([1,2,4])
# 第一维度不变,其他两维就当作矩阵做乘法
# unsqueeze(0)用以在在第一维扩充维度
# attn_applied赋予encoder_outputs不同部分不同权重
attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0),
encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0)) # 计算两个矩阵的乘积
output = torch.cat((embedded[0], attn_applied[0]), 1) # 按列拼接 embedded[0]和embedded[1]
output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0)
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1)
return output, hidden, attn_weights
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
def tensorsFromPair(pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5
def train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
# 初始化隐藏状态
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
# 梯度清零
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
input_length = input_tensor.size(0)
target_length = target_tensor.size(0)
# 初始化,等会替换
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
loss = 0
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(
input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
# encoder_output.size() ==> tensor([1,1,hidden_size])
encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0]
# 输入为<sos>,decoder初始隐藏状态为encoder的
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
# 随机决定是否采用teacher_forcing
use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False
if use_teacher_forcing:
# 若采用,label作为下一个时间步输入
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
else:
# 若不用,则用预测出的作为Decoder下一个输入
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
# topk代表在所给维度上输出最大值
# 参数代表输出前多少个最大值
# 若为1,就是最大值
# topv,topi 分别为前n个最大值和其对应的索引
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
# squeeze()进行降维
# detach将与这个变量相关的从计算图中剥离
# 从而减少内存的开销
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach()
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
# 若某个时间步输入为<eos>,则停止
if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token:
break
loss.backward()
# 参数更新
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
# 返回平均loss
return loss.item() / target_length
import time
import math
def asMinutes(s):
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
def timeSince(since, percent):
now = time.time()
s = now - since
es = s / (percent)
rs = es - s
return '%s (- %s)' % (asMinutes(s), asMinutes(rs))
def trainIters(encoder, decoder, n_iters, print_every=1000, plot_every=100, learning_rate=0.01):
start = time.time()
plot_losses = []
# 每一次重置
print_loss_total = 0
plot_loss_total = 0
# 定义优化器
encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# random.choice(pairs)随机选择
training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs)) for i in range(n_iters)]
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1):
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor = training_pair[0]
target_tensor = training_pair[1]
loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder,
decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion)
print_loss_total += loss
plot_loss_total += loss
# 若能整除,就打印此时训练进度
if iter % print_every == 0:
print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every
print_loss_total = 0
print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start, iter / n_iters),
iter, iter / n_iters * 100, print_loss_avg))
# 若能整除,则把平均损失加入plot_loss
# 为后期画图做准备
if iter % plot_every == 0:
plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every
plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg)
plot_loss_total = 0
showPlot(plot_losses)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
import numpy as np
def showPlot(points):
plt.figure()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
loc = ticker.MultipleLocator(base=0.2)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(loc)
plt.plot(points)
def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
# 评估时停止梯度跟踪,减少内存
with torch.no_grad():
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence)
input_length = input_tensor.size()[0]
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) # SOS
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
decoded_words = []
decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length)
for di in range(max_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data
topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1)
if topi.item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('<EOS>')
break
else:
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()])
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach()
return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1]
def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=10):
for i in range(n):
pair = random.choice(pairs)
print('>', pair[0])
print('=', pair[1])
output_words, attentions = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0])
output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words)
print('<', output_sentence)
print('')
hidden_size = 256
encoder1 = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device)
attn_decoder1 = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device)
trainIters(encoder1, attn_decoder1, 75000, print_every=5000)
# 保留网络参数,注意是实例化之后的
torch.save(encoder1.state_dict(), "encoder_parameters")
torch.save(attn_decoder1.state_dict(), "decoder_parameters")
# 注意力可视化
def showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions):
# 用colorbar设置图
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
# attentions出来之后是tensor形式,需要转换为numpy
cax = ax.matshow(attentions.numpy(), cmap='bone')
fig.colorbar(cax)
# 设置坐标
ax.set_xticklabels([''] + input_sentence.split(' ') +
['<EOS>'], rotation=90)
ax.set_yticklabels([''] + output_words)
# 在每个刻度处显示标签,刻度为1的倍数
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
plt.show()
def evaluateAndShowAttention(input_sentence):
output_words, attentions = evaluate(
encoder1, attn_decoder1, input_sentence)
print('input =', input_sentence)
print('output =', ' '.join(output_words))
showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions)
evaluateAndShowAttention("他比我高两寸。")
#evaluateAndShowAttention("我赢了 。")
#evaluateAndShowAttention("我们来试试 。")
#evaluateAndShowAttention("为什么是我 ?")
decoder_hidden = [10, 5, 10]








