问题背景
安卓日常开发和学习过程中,涉及图片压缩的场景很多,比如图片上传过程等。很多时候加载的图片过多不进行图片压缩的话也是很容易出现OOM内存溢出的,本文将对安卓开发的图片压缩操作以及鲁班压缩框架进行初步的介绍,以及对鲁班压缩的源码进行初步的梳理。
问题分析
首先,介绍下安卓开发中常见的几种压缩方式:
1.质量压缩
质量压缩
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 60, outputStream)
或者采样率压缩
val options = BitmapFactory.Options()
options.inSampleSize = 2
val compressedBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(pathName, options)
2.色彩压缩
val options = BitmapFactory.Options()
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565
// 压缩成RGB_565的色彩编码方式
val compressedBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(pathName,options)
3.裁剪压缩
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path)
val matrix = Matrix()
matrix.setScale(0.5f, 0.5f)
val scaledBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, bitmap.width / 2, bitmap.height / 2, matrix, true)
Android中比较知名的图片压缩框架是Luban和Compressor。Luban的压缩算法听说是根据微信图片压缩逆推的;Compressor则支持Kotlin的协程。 Luban开源地址:https://github.com/Curzibn/Luban Compressor开源地址:https://github.com/zetbaitsu/Compressor
下面介绍luban压缩的简单使用。
(1)导入依赖:
implementation 'top.zibin:Luban:1.1.8'
(2)鲁班提供的方法列表
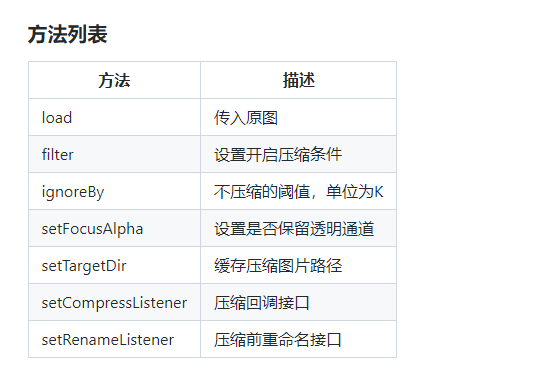 (3)异步调用
Luban内部采用IO线程进行图片压缩,外部调用只需设置好结果监听即可:
(3)异步调用
Luban内部采用IO线程进行图片压缩,外部调用只需设置好结果监听即可:
Luban.with(this)
.load(photos)
.ignoreBy(100)
.setTargetDir(getPath())
.filter(new CompressionPredicate() {
@Override
public boolean apply(String path) {
return !(TextUtils.isEmpty(path) || path.toLowerCase().endsWith(".gif"));
}
})
.setCompressListener(new OnCompressListener() {
@Override
public void onStart() {
// TODO 压缩开始前调用,可以在方法内启动 loading UI
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(File file) {
// TODO 压缩成功后调用,返回压缩后的图片文件
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
// TODO 当压缩过程出现问题时调用
}
}).launch();
问题解决
上面介绍了鲁班压缩的基本使用,下面对鲁班压缩的源码进行初步梳理。 (1)结合上面的使用代码,我们先看看with()方法 top.zibin.luban.Luban#with
public static Builder with(Context context) {
return new Builder(context);
}
top.zibin.luban.Luban.Builder#Builder
public static class Builder {
private Context context;
private String mTargetDir;
private boolean focusAlpha;
private int mLeastCompressSize = 100;
private OnRenameListener mRenameListener;
private OnCompressListener mCompressListener;
private CompressionPredicate mCompressionPredicate;
private List<InputStreamProvider> mStreamProviders;
Builder(Context context) {
this.context = context;
this.mStreamProviders = new ArrayList<>();
}
private Luban build() {
return new Luban(this);
}
...
可以看到,luban压缩的构建使用了builder模式,我们看下上面的build方法。 top.zibin.luban.Luban.Builder#build
private Luban build() {
return new Luban(this);
}
top.zibin.luban.Luban#Luban
private Luban(Builder builder) {
this.mTargetDir = builder.mTargetDir;
this.mRenameListener = builder.mRenameListener;
this.mStreamProviders = builder.mStreamProviders;
this.mCompressListener = builder.mCompressListener;
this.mLeastCompressSize = builder.mLeastCompressSize;
this.mCompressionPredicate = builder.mCompressionPredicate;
mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper(), this);
}
可以看到,Luban通过builder模式给成员变量赋值,同时构造了一个主线程的handler,并自己实现了handler的回调callback接口。 (2)跳过中间builder模式设置的属性,有兴趣的可以自己点进去看看细节。我们现在一起看看最后的launch()方法。 top.zibin.luban.Luban.Builder#launch
/**
* begin compress image with asynchronous
*/
public void launch() {
build().launch(context);
}
top.zibin.luban.Luban#launch
private void launch(final Context context) {
if (mStreamProviders == null || mStreamProviders.size() == 0 && mCompressListener != null) {
mCompressListener.onError(new NullPointerException("image file cannot be null"));
}
Iterator<InputStreamProvider> iterator = mStreamProviders.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
final InputStreamProvider path = iterator.next();
// 遍历文件,通过AsyncTask开启子线程去对文件进行压缩。
AsyncTask.SERIAL_EXECUTOR.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_COMPRESS_START));
File result = compress(context, path);
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_COMPRESS_SUCCESS, result));
} catch (IOException e) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_COMPRESS_ERROR, e));
}
}
});
iterator.remove();
}
}
看launch()方法的代码,对加载进来的文件进行一个遍历,然后对每个文件开启一个子线程去进行压缩,一起看下压缩逻辑。 top.zibin.luban.Luban#compress
private File compress(Context context, InputStreamProvider path) throws IOException {
File result;
File outFile = getImageCacheFile(context, Checker.SINGLE.extSuffix(path));
if (mRenameListener != null) {
String filename = mRenameListener.rename(path.getPath());
outFile = getImageCustomFile(context, filename);
}
if (mCompressionPredicate != null) {
if (mCompressionPredicate.apply(path.getPath())
&& Checker.SINGLE.needCompress(mLeastCompressSize, path.getPath())) {
// 判断需要压缩
result = new Engine(path, outFile, focusAlpha).compress();
} else {
result = new File(path.getPath());
}
} else {
result = Checker.SINGLE.needCompress(mLeastCompressSize, path.getPath()) ?
new Engine(path, outFile, focusAlpha).compress() :
new File(path.getPath());
}
return result;
}
压缩逻辑对mCompressionPredicate和mLeastCompressSize进行一个判断,当符合压缩条件时,去进行压缩操作,看下压缩的具体逻辑。 top.zibin.luban.Engine#compress
File compress() throws IOException {
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inSampleSize = computeSize();
// 1、采样压缩
Bitmap tagBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(srcImg.open(), null, options);
ByteArrayOutputStream stream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
if (Checker.SINGLE.isJPG(srcImg.open())) {
tagBitmap = rotatingImage(tagBitmap, Checker.SINGLE.getOrientation(srcImg.open()));
}
// 2、质量压缩
tagBitmap.compress(focusAlpha ? Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG : Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 60, stream);
tagBitmap.recycle();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(tagImg);
fos.write(stream.toByteArray());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
stream.close();
return tagImg;
}
由上面的压缩方法可以看出,一次鲁班压缩包括一次采样压缩和一次60的图片质量压缩。 下面看下采样压缩的采样率获取逻辑: top.zibin.luban.Engine#computeSize
private int computeSize() {
srcWidth = srcWidth % 2 == 1 ? srcWidth + 1 : srcWidth;
srcHeight = srcHeight % 2 == 1 ? srcHeight + 1 : srcHeight;
int longSide = Math.max(srcWidth, srcHeight);
int shortSide = Math.min(srcWidth, srcHeight);
float scale = ((float) shortSide / longSide);
if (scale <= 1 && scale > 0.5625) {
if (longSide < 1664) {
return 1;
} else if (longSide < 4990) {
return 2;
} else if (longSide > 4990 && longSide < 10240) {
return 4;
} else {
return longSide / 1280 == 0 ? 1 : longSide / 1280;
}
} else if (scale <= 0.5625 && scale > 0.5) {
return longSide / 1280 == 0 ? 1 : longSide / 1280;
} else {
return (int) Math.ceil(longSide / (1280.0 / scale));
}
}
这个算法比较复杂,作者的意思是对微信朋友圈100图片的压缩结果进行最大适配接近的结果值,有兴趣可以深入了解下。
问题总结
本文对安卓开发的图片压缩操作以及鲁班压缩框架进行了初步的介绍,以及对鲁班压缩的源码进行初步的梳理,后面会继续对图片压缩开源框架 Compressor进行介绍,有兴趣的同学可以进一步深入研究。










