文章目录
引言
本文将演示无向图非连通图的深度优先生成森林
无向图的极小连通子图称为生成树,将无向图非连通图的各生成树结合起来构造生成森林
由深度优先搜索得到的生成树称为深度优先生成树
由广度优先搜索得到的称为广度优先生成树
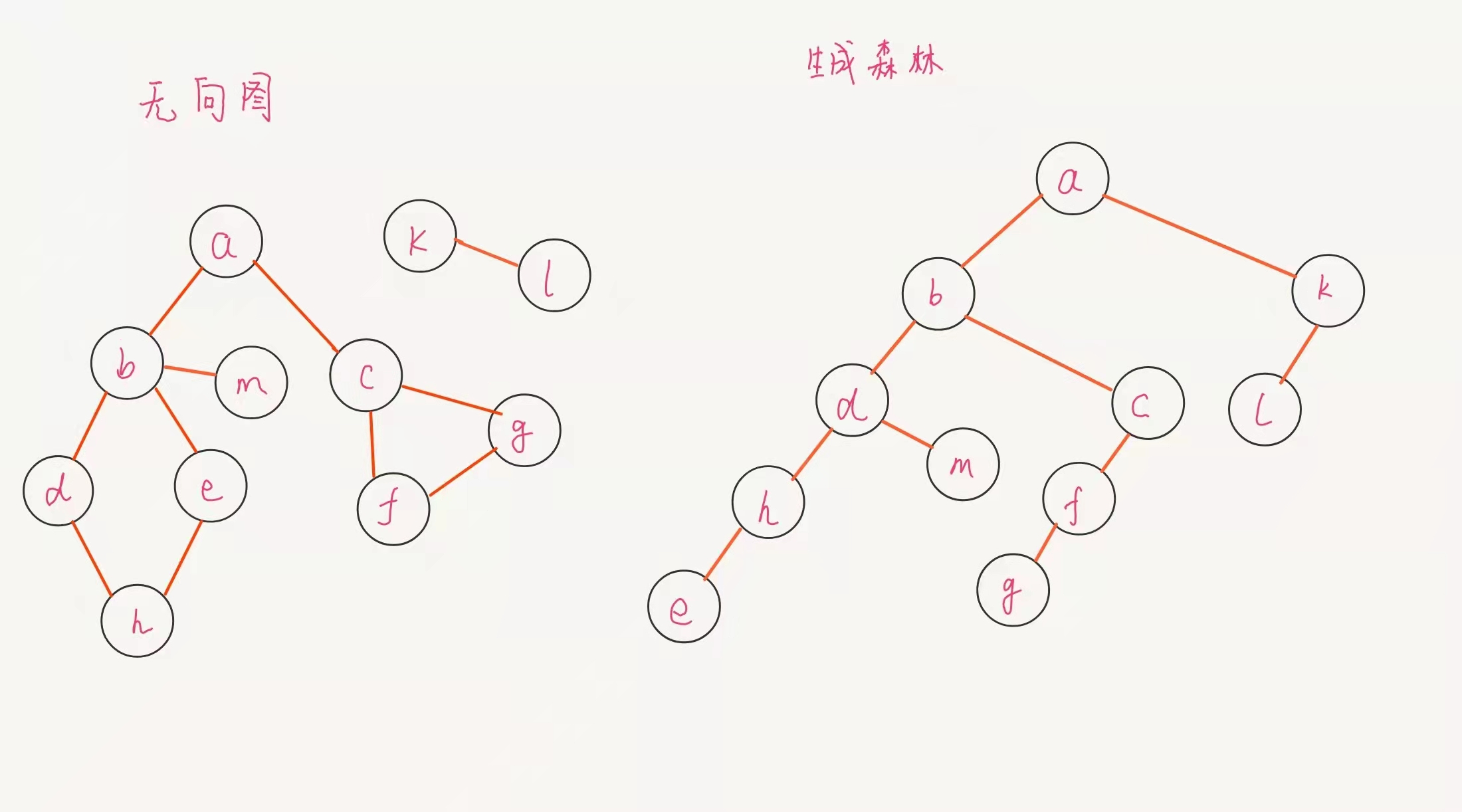 深度优先遍历结果对应森林的先序遍历
深度优先遍历结果对应森林的先序遍历
本文选择孩子兄弟表示法作为森林的存储结构
阅读前请确保您知道树的孩子兄弟表示法及图的深度优先遍历
【数据结构 | C语言】树的存储结构(双亲表示法、带双亲的结点表示法、结点兄弟表示法) C语言实现
【数据结构 | C语言】图的遍历(深度优先、广度优先)C语言
注:在图的遍历一文中,遍历的是连通图,非连通图的遍历不需要指定开始结点,用for循环找到未遍历的结点即可(在本文完整代码中有)
算法
// 深度优先生成树的构造算法,类似于深夜优先搜索。在搜索过程中,逐渐构造森林结点
// 如果不理解此算法,建议与深度优先搜索算法对比起来,观察两个之间的区别
// 这个函数构造了森林的各树根结点
void SpanningTree(pGraph graph, pForest *forest) {
// 访问标志数组
bool searched[MAX_SIZE];
for (int i=0; i<MAX_SIZE; i++)
searched[i] = false;
// 森林结点 p 指向森林的最后一颗树的根结点
// 在第一次生成森林根结点时,给 p 赋值。预先在这定义,是防止编译错误
pForest p;
// 遍历全部结点,搜索未被访问的结点
for (int i=0; i<graph->vexnum; i++) {
if (searched[i] == false) {
// 如果根结点为空,生成森林根结点
if (*forest == NULL) {
pForest p = CreateForest(graph->vertices[i].data);
*forest = p;
} else { // 否则,创建 p 的兄弟结点
p->nextsibling = CreateForest(graph->vertices[i].data);
p = p->nextsibling;
}
// 递归构造森林的结点
SpanningVisit(graph, i, searched, p);
}
}
}
// SpanningTree 传过来的p是根
// 这个函数构造了树结点
void SpanningVisit(pGraph graph, int i, bool *searched, pForest forest) {
searched[i] = true;
// first 用来判断是否有孩子
// 如果没有孩子结点,生成孩子结点
// 否则,生成兄弟结点
bool first = true;
// q 指向最后一个兄弟结点。如果理解森林的遍历,这个很容易理解
/*
在递归过程中,每向下一层,就会生成该层的 q,每层的 q 都指向最后一个兄弟结点
如果退出该层,q就指回上一层的最后一个兄弟结点。每层的 q 值都是不同的
*/
pForest q;
// 找到结点的第一个邻结点
ArcNode *p = graph->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (p!=NULL) {
// 如果未访问过
if (searched[p->index] == false) {
// 没有孩子就生成孩子,否则,生成孩子兄弟
if (first) {
q = CreateForest(graph->vertices[p->index].data);
forest->child = q;
first = false; // 已经有孩子了
} else {
q->nextsibling = CreateForest(graph->vertices[p->index].data);
q = q->nextsibling;
}
// if 结束后,不管走哪边,q 都指向最后一个兄弟结点了
SpanningVisit(graph, p->index, searched, q);
}
// 指向下一个邻接点
p = p->nextArc;
}
}
完整代码(复制粘贴可用)
/*
深度优先生成森林
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 20
#define true 1
#define false 0
typedef char ElemType;
typedef int bool;
typedef struct ArcNode ArcNode;
// forest
typedef struct Forest {
ElemType val;
struct Forest *child, *nextsibling;
} Forest, *pForest;
// graph
struct ArcNode {
int index;
ArcNode *nextArc;
};
typedef struct {
ElemType data;
ArcNode *firstArc;
} VNode, AdjList[MAX_SIZE];
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum, arcnum;
} Graph, *pGraph;
// 森林的函数
pForest CreateForest(ElemType val);
void AddNode(pForest *forest, ElemType val);
void PreOrderForest(pForest forest);
// 图的函数
pGraph CreateGraph();
void AddVex(pGraph graph, ElemType vex);
void AddArc(pGraph graph, ElemType vexa, ElemType vexb);
// 深度优先遍历图
void DeepFirstSearch(pGraph graph);
void Visit(pGraph graph, int i, bool *searched);
// 生成森林
void SpanningTree(pGraph graph, pForest *forest);
void SpanningVisit(pGraph graph, int i, bool *searched, pForest forest);
int main() {
// 创建图
pGraph graph = CreateGraph();
// 添加结点
AddVex(graph, 'a');
AddVex(graph, 'b');
AddVex(graph, 'c');
AddVex(graph, 'd');
AddVex(graph, 'e');
AddVex(graph, 'f');
AddVex(graph, 'g');
AddVex(graph, 'h');
AddVex(graph, 'k');
AddVex(graph, 'l');
AddVex(graph, 'm');
// 添加边
AddArc(graph, 'a', 'b');
AddArc(graph, 'a', 'c');
AddArc(graph, 'b', 'd');
AddArc(graph, 'b', 'e');
AddArc(graph, 'd', 'h');
AddArc(graph, 'e', 'h');
AddArc(graph, 'c', 'f');
AddArc(graph, 'c', 'g');
AddArc(graph, 'f', 'g');
AddArc(graph, 'b', 'm');
AddArc(graph, 'k', 'l');
// 深度优先遍历
DeepFirstSearch(graph);
// 生成森林
pForest forest;
forest = NULL;
SpanningTree(graph, &forest);
// 先序遍历森林
PreOrderForest(forest);
return 0;
}
pForest CreateForest(ElemType val) {
pForest new = (pForest)malloc(sizeof(Forest));
memset(new, 0, sizeof(Forest));
new->val = val;
return new;
}
void AddNode(pForest *forest, ElemType val) {
pForest new = CreateForest(val);
*forest = new;
}
void PreOrderForest(pForest forest) {
if (forest) {
printf("%c\t", forest->val);
PreOrderForest(forest->child);
PreOrderForest(forest->nextsibling);
}
}
pGraph CreateGraph() {
pGraph new = (pGraph)malloc(sizeof(Graph));
memset(new, 0, sizeof(Graph));
return new;
}
void AddVex(pGraph graph, ElemType vex) {
graph->vertices[graph->vexnum++].data = vex;
}
void AddArc(pGraph graph, ElemType vexa, ElemType vexb) {
// 找到 a 和 b 结点
int index_a, index_b;
for (int i = 0; i < graph->vexnum; i++) {
if (graph->vertices[i].data == vexa)
index_a = i;
if (graph->vertices[i].data == vexb)
index_b = i;
}
// 添加边
ArcNode *newa = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
memset(newa, 0, sizeof(ArcNode));
newa->index = index_b;
if (graph->vertices[index_a].firstArc == NULL)
graph->vertices[index_a].firstArc = newa;
else {
ArcNode *p = graph->vertices[index_a].firstArc;
while (p->nextArc != NULL)
p = p->nextArc;
p->nextArc = newa;
}
// 另一个边
ArcNode *newb = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
memset(newb, 0, sizeof(ArcNode));
newb->index = index_a;
if (graph->vertices[index_b].firstArc == NULL)
graph->vertices[index_b].firstArc = newb;
else {
ArcNode *p = graph->vertices[index_b].firstArc;
while (p->nextArc != NULL)
p = p->nextArc;
p->nextArc = newb;
}
graph->vexnum++;
}
void DeepFirstSearch(pGraph graph) {
// 标志数组
bool searched[MAX_SIZE];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)
searched[i] = false;
// 遍历图
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)
if (searched[i] == false)
Visit(graph, i, searched);
printf("\n");
}
void Visit(pGraph graph, int i, bool *searched) {
// output
searched[i] = true;
printf("%c\t", graph->vertices[i].data);
ArcNode *p = graph->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (p != NULL) {
if (searched[p->index] == false)
Visit(graph, p->index, searched);
p = p->nextArc;
}
}
void SpanningTree(pGraph graph, pForest *forest) {
// 访问标志数组
bool searched[MAX_SIZE];
for (int i=0; i<MAX_SIZE; i++)
searched[i] = false;
// 传递结点
pForest p;
for (int i=0; i<graph->vexnum; i++) {
if (searched[i] == false) {
// 如果根结点为空
if (*forest == NULL) {
p = CreateForest(graph->vertices[i].data);
*forest = p;
} else { // 否则,创建 p 的兄弟结点
p->nextsibling = CreateForest(graph->vertices[i].data);
p = p->nextsibling;
}
SpanningVisit(graph, i, searched, p);
}
}
}
// SpanningTree 传过来的p是根
void SpanningVisit(pGraph graph, int i, bool *searched, pForest forest) {
searched[i] = true;
bool first = true;
pForest q;
// 找到结点的第一个邻结点
ArcNode *p = graph->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (p!=NULL) {
// 如果未访问过
if (searched[p->index] == false) {
if (first) {
q = CreateForest(graph->vertices[p->index].data);
forest->child = q;
first = false;
} else {
q->nextsibling = CreateForest(graph->vertices[p->index].data);
q = q->nextsibling;
}
SpanningVisit(graph, p->index, searched, q);
}
p = p->nextArc;
}
}










