目录
一 . 什么是链表?

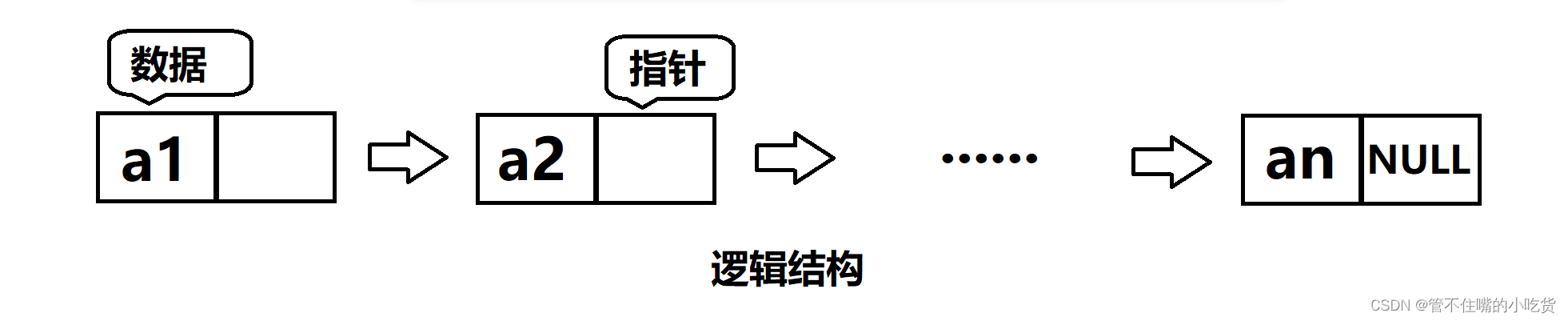
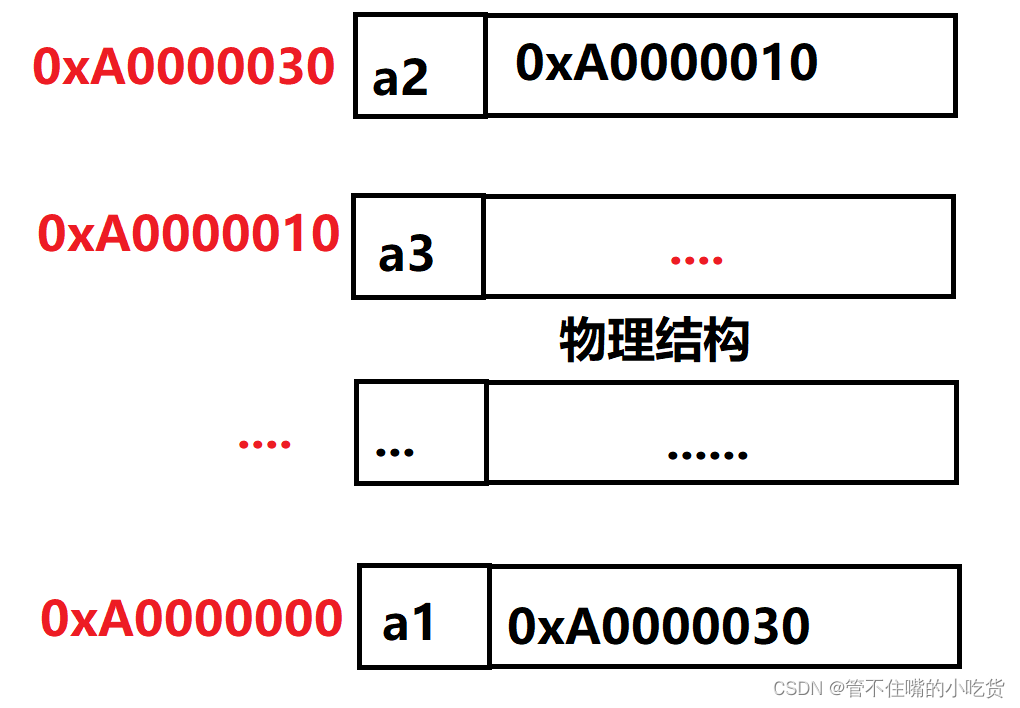
二 . 实现单链表
(1)创建相关源文件和头文件
(2)定义结构体
//结构体数据类型重定义,方便我们更改要存储的元素类型
typedef int SLTDataType;
struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data; //要存储的数据——数据域
struct SListNode* next; //用来存储下一个结构体的地址——指针域
};
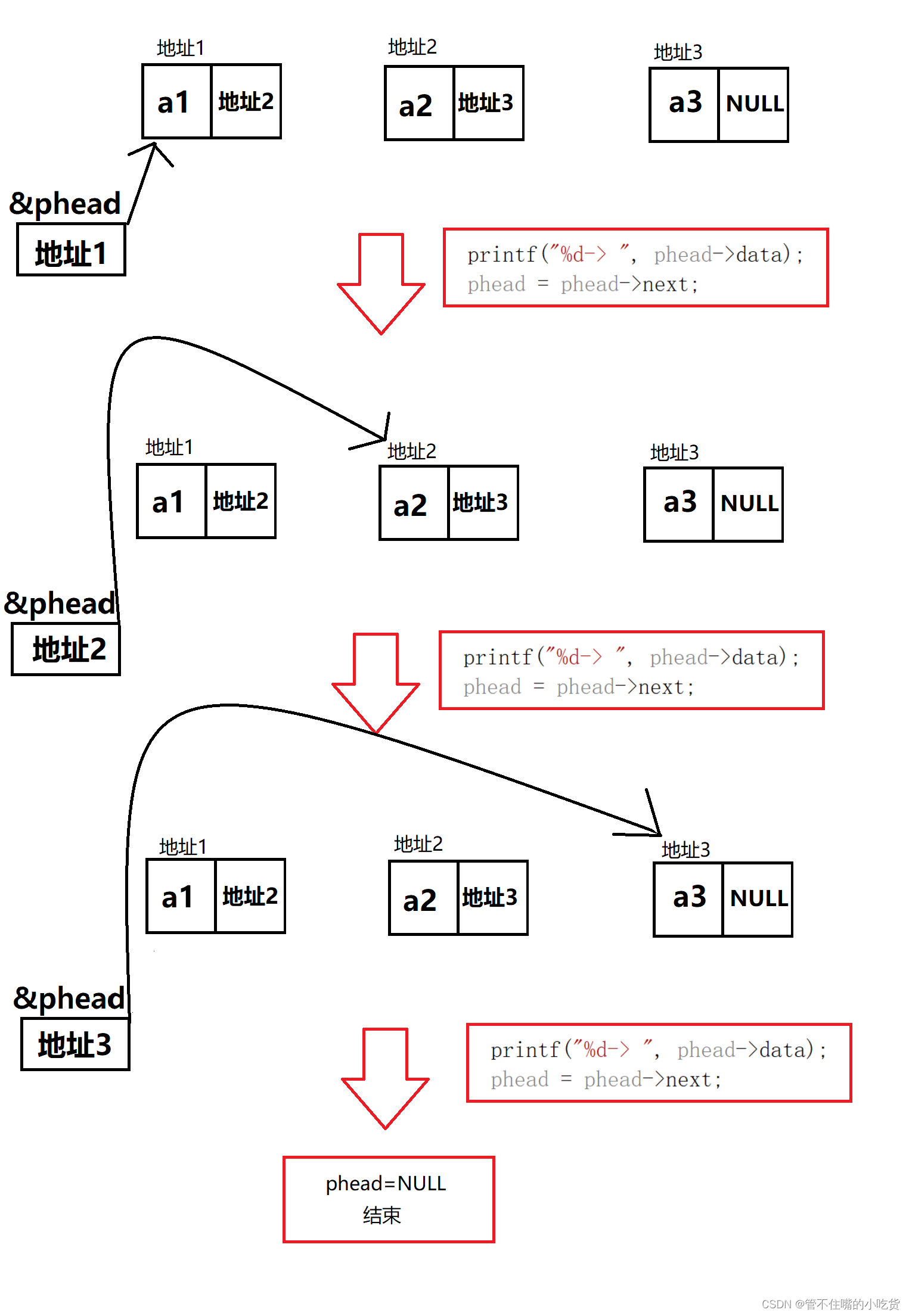
(3)打印单链表(SListPrint)
//打印链表
void SListPrint(struct SListNode* phead)
{
while (phead)
{
printf("%d-> ", phead->data);
phead = phead->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
} 
(4)创建新结点(BuyListNode)
要插入新数据,我们就要生成一个新的结点。
//生成新节点
struct SListNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
//调用maoolc()函数生成一个结点
struct SListNode* newNode = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));
//如果申请失败,打印错误并结束程序
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
exit(-1);
}
//将要插入的数据赋给新结点
newNode->data = x;
//新节点的next置空
newNode->next = NULL;
//返回生成的结点的地址
return newNode;
}(5) 尾插(SListPushBack)
//尾插
void SListPushBack(struct SListNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成一个新的结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//当链表为空,直接把新结点地址赋给*pphead
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//设置一个tail指针用来找到尾部结点
struct SListNode* tail = *pphead;
//不断循环,直到找到尾部结点
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;//指向下一个结点
}
//让原本置空的指针指向新生成的结点
tail->next = newnode;
}
}(6)头插(SListPushFront)
//头插
void SListPushFront(struct SListNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成新结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//保存原来第一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = *pphead;
//让头指向新结点
*pphead = newnode;
//指向原来的头结点
newnode->next = prev;
}(7)尾删( SListPopBack)
//尾删
void SListPopBack(struct SListNode** pphead)
{
//如果链表为空,就直接返回空,也可以使用assert(*pphead!=NULL)
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
//如果只有一个结点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
//找尾部
struct SListNode* tail = *pphead;
//记录尾部的前一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = NULL;
//找尾部结点,并保存尾部结点的前一个结点的地址
while (tail->next)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
//找到尾部结点,释放
free(tail);
//置空
tail = NULL;
//把尾部的前一个结点保存的地址置空
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
(8)头删(SListPopFront)
//头删
void SListPopFront(struct SListNode** pphead)
{
//如果链表为空,返回空,也可以使用assert(*pphead!=NULL)
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
//找到下一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = (*pphead)->next;
//释放第一个结点
free(*pphead);
//头指针指向第二个结点
*pphead = prev;
}
}(9)查找数据(SListFind)
//查找
struct SListNode* SListFind(struct SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
struct SListNode* cur = phead;
//循环查找
while (cur)
{
//找到返回该结点地址
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
//没找到指向下一个结点
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
//如果没找到,返回NULL
return NULL;
}//查找多个相同的数据
while (pos)
{
printf("第%d个pos节点:%p->%d\n", i++, pos, pos->data);
//pos指向目标结点的下一个结点
pos = SListFind(pos->next, 50);
}
(10)指定位置插入
先看前面的:我们可以使用指针来找到pos的前一个结点,在进行插入(我们可以使用SListFind)
//指定结点前插入
void SListInsertF(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成一个新的结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//只有一个结点或者链表为空,进行头插
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//设计一个结构体指针来找pos的前一个结点
struct SListNode* posprev = *pphead;
while (posprev->next != pos)
{
posprev = posprev->next;
}
posprev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}再看后面的:
//指定结点后插入
void SListInsertB(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成一个新的结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//新结点指针域指向该结点的后一个
newnode->next = pos->next;
//结点的指针域指向新结点
pos->next = newnode;
}(11)指定位置删除(指定位置删除)
//指定位置删除
void SListEarse(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos)
{
//如果链表为空,返回空,也可以使用assert(*pphead!=NULL)
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
//要删除的结点是第一个结点
if (pos == *pphead)
{
//找到下一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = (*pphead)->next;
//释放第一个结点
free(*pphead);
//头指针指向第二个结点
*pphead = prev;
}
else
{
//要找到pos结点的前一个结点位置
struct SListNode* posprev = *pphead;
while (posprev->next != pos)
{
posprev = posprev->next;
}
//让posprev的指针域指向下下个结点
posprev->next = pos->next;
//释放结点pos的空间
free(pos);
//置空
pos = NULL;
}
}(12)清空链表(SListDestory)
void SListDestory(struct SListNode** pphead)
{
struct SListNode* prev = *pphead;
while ((*pphead) != NULL)
{
//找到头指针指向的结点
prev = *pphead;
//让头指针指向下一个结点
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
//释放前面的结点
free(prev);
}
}三. 完整代码
SingleLinkedList.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
//结构体数据类型重定义,方便我们更改要存储的元素类型
typedef int SLTDataType;
struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data; //要存储的数据(数据域)
struct SListNode* next; //用来存储下一个结构体的地址(指针域)
};
//打印
void SListPrint(struct SListNode* phead);
//创建一个新节点
struct SListNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x);
//尾部插入
void SListPushBack(struct SListNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//头部插入
void SListPushFront(struct SListNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//尾部删除
void SListPopBack(struct SListNode** pphead);
//头部删除
void SListPopFront(struct SListNode** pphead);
//查找,返回对应结点地址
//int SListFind(struct SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
struct SListNode* SListFind(struct SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
//指定插入(还有一种按输入位置来插入)(在前面插入)
void SListInsertF(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//后
void SListInsertB(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//指定删除
void SListEarse(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos);
//销毁链表
void SListDestory(struct SListNode** pphead);SingleLinkedList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "SingleLinkedList.h"
//打印链表
void SListPrint(struct SListNode* phead)
{
while (phead)
{
printf("%d-> ", phead->data);
phead = phead->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//生成新节点
struct SListNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
//调用maoolc()函数生成一个结点
struct SListNode* newNode = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));
//如果申请失败,打印错误并结束程序
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
exit(-1);
}
//将要插入的数据赋给新结点
newNode->data = x;
//新节点的next置空
newNode->next = NULL;
//返回生成的结点的地址
return newNode;
}
//尾插
void SListPushBack(struct SListNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成一个新的结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//如果链表为空,直接把新结点地址赋给*pphead
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//设置一个指针tail用来找到尾部结点
struct SListNode* tail = *pphead;
//不断循环,直到找到尾部结点
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;//指向下一个结点
}
//让原本置空的指针指向新生成的结点
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
//头插
void SListPushFront(struct SListNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成新结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//保存原来第一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = *pphead;
//让头指向新结点
*pphead = newnode;
newnode->next = prev;
}
//尾删
void SListPopBack(struct SListNode** pphead)
{
//如果链表为空,就直接返回空,也可以使用assert(*pphead!=NULL)
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
//如果只有一个结点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
//找尾部
struct SListNode* tail = *pphead;
//记录尾部的前一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = NULL;
//找尾部结点,并保存尾部结点的前一个结点的地址
while (tail->next)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
//找到尾部结点,释放空间
free(tail);
//置空
tail = NULL;
//把尾部的前一个结点保存的地址置空
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
//头删
void SListPopFront(struct SListNode** pphead)
{
//如果链表为空,返回空,也可以使用assert(*pphead!=NULL)
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
//找到下一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = (*pphead)->next;
//释放第一个结点
free(*pphead);
//头指针指向第二个结点
*pphead = prev;
}
}
//查找
struct SListNode* SListFind(struct SListNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
struct SListNode* cur = phead;
//循环查找
while (cur)
{
//找到返回该结点地址
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
//没找到指向下一个结点
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
//如果没找到,返回NULL
return NULL;
}
//指定结点前插入
void SListInsertF(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成一个新的结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//只有一个结点或者链表为空,进行头插
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//设计一个结构体指针来找pos的前一个结点
struct SListNode* posprev = *pphead;
while (posprev->next != pos)
{
posprev = posprev->next;
}
posprev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
//指定结点后插入
void SListInsertB(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
//生成一个新的结点
struct SListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
//新结点指针域指向该结点的后一个
newnode->next = pos->next;
//结点的指针域指向新结点
pos->next = newnode;
}
//指定位置删除
void SListEarse(struct SListNode** pphead, struct SListNode* pos)
{
//如果链表为空,返回空,也可以使用assert(*pphead!=NULL)
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
//要删除的结点是第一个结点
if (pos == *pphead)
{
//找到下一个结点的地址
struct SListNode* prev = (*pphead)->next;
//释放第一个结点
free(*pphead);
//头指针指向第二个结点
*pphead = prev;
}
else
{
//要找到pos结点的前一个结点位置
struct SListNode* posprev = *pphead;
while (posprev->next != pos)
{
posprev = posprev->next;
}
//让posprev的指针域指向下下个结点
posprev->next = pos->next;
//释放结点pos的空间
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}
//清空链表
void SListDestory(struct SListNode** pphead)
{
struct SListNode* prev = *pphead;
while ((*pphead) != NULL)
{
//找到头指针指向的结点
prev = *pphead;
//让头指针指向下一个结点
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
//释放前面的结点
free(prev);
}
}Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "SingleLinkedList.h"
void text1()
{
struct SListNode* head = NULL;///初始化头指针
SListPushFront(&head, 5);
SListPushFront(&head, 50);
SListPushFront(&head, 50);
SListPushFront(&head, 5);
struct SListNode* pos = SListFind(head, 50);
int i = 1;
//查找多个相同的值
while (pos)
{
printf("第%d个pos节点:%p->%d\n", i++, pos, pos->data);
//pos指向目标结点的下一个结点
pos = SListFind(pos->next, 50);
}
SListPrint(head);
//修改
pos = SListFind(head, 50);
if (pos)
{
pos->data = 30;
}
SListPrint(head);
}
void text2()
{
struct SListNode* head = NULL;
//插入
SListPushBack(&head, 2);
SListPushBack(&head, 5);
SListPushBack(&head, 15);
//查找14位置
struct SListNode* pos = SListFind(head, 14);
//判断是否有14
if (pos == NULL)
{
printf("没有该数据\n");
}
else
{
//删除14
SListEarse(&head, pos);
}
SListPrint(head);
//清空
SListDestory(&head);
//插入
SListPushBack(&head, 2);
SListPushBack(&head, 5);
SListPrint(head);
}
int main()
{
//text1();
text2();
return 0;
}四. 总结
OK!单链表的实现就到这里了,感谢大家!











