基本介绍
Thrift 是用于点对点 RPC 实现的轻量级、独立于语言的软件堆栈。 Thrift 为数据传输、数据序列化和应用程序级处理提供了清晰的抽象和实现。 代码生成系统将简单的定义语言作为输入,并生成跨编程语言的代码,这些编程语言使用抽象堆栈来构建可互操作的 RPC 客户端和服务器。
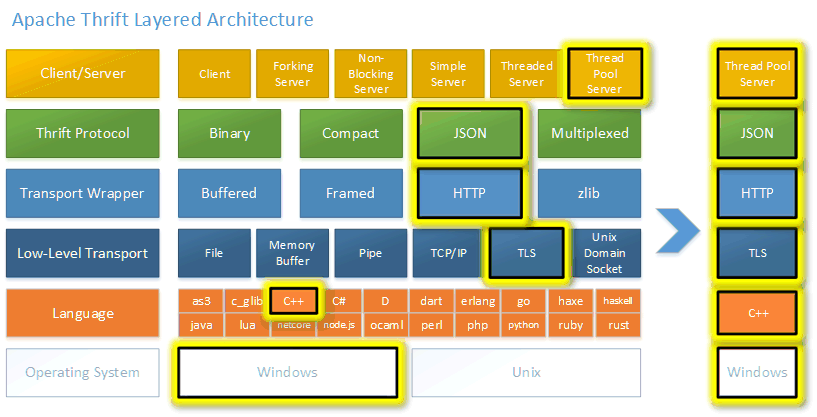
Thrift 使以不同编程语言编写的程序可以轻松共享数据和调用远程过程。 Thrift 支持 28 种编程语言,很有可能支持您当前使用的语言。
Thrift 专门设计用于支持跨客户端和服务器代码的非原子版本更改。 这使您可以升级服务器,同时仍然能够为旧客户端提供服务; 或让较新的客户端向较旧的服务器发出请求。 在 Thrift Missing Guide 中可以找到社区提供的关于在版本化 API 时节俭和兼容性的优秀文章。
下载与编译thrift
在使用Thrift之前,还需要安装编译器,如果是windows系统,那么可以直接下载二进制版本的thrift编译器,例如下述为0.16.0 windwos版本的thrift编译器
- Thrift compiler for Windows (thrift-0.16.0.exe)
而如果你使用的是linux系统,那么你可以从源码进行编译安装,源码下载地址以及源码编译方法可见如下链接:
- 源码下载地址:thrift-0.16.0.tar.gz
- 源码编译方法:https://thrift.apache.org/docs/BuildingFromSource
当然,如果你使用的是Java语言,那么还需要在你的项目中添加如下依赖以完全使用thrift提供的能力。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift</groupId>
<artifactId>libthrift</artifactId>
<version>0.16.0</version>
</dependency>下面以Java语言的maven项目为例,讲述从头构建一个基本的thrift应用。
如果您对如何使用thrift定义语言不太了解,那么可以参考文章:Thrift接口定义语言
而对于thrift中所使用的基本类型,您可以参考文章:Thrift数据类型
构建thrift基本应用
在安装了Thrift编译器之后,我们需要创建一个.thrift文件,该文件是一个接口定义,由 thrift 类型和 Services 组成。 在此文件中定义的服务由服务端实现并由任何客户端调用。 Thrift 编译器用于将您的 Thrift 文件生成为源代码,供不同的客户端库和您编写的服务端使用。
Apache Thrift 允许您在一个简单的定义文件中定义数据类型和服务接口。 将该文件作为输入,编译器生成代码,用于轻松构建跨编程语言无缝通信的 RPC 客户端和服务器。 无需编写大量样板代码来序列化和传输对象并调用远程方法,您可以直接开始工作。
您可以通过如下方式生成源代码:
thrift --gen <language> <Thrift filename>本文中,由于我们使用的是maven项目,我们可以使用maven插件来完成.thrift文件编译工作。
我们定义两个.thrift文件,一个名为shared.thrift,另一个名为tutorial.thrift,以此说明如何编写.thrift文件。
shared.thrift
/**
* This Thrift file can be included by other Thrift files that want to share
* these definitions.
*/
namespace java com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial
struct SharedStruct {
1: i32 key
2: string value
}
service SharedService {
SharedStruct getStruct(1: i32 key)
}tutorial.thrift
# Thrift Tutorial
# Mark Slee (mcslee.com)
#
# This file aims to teach you how to use Thrift, in a .thrift file. Neato. The
# first thing to notice is that .thrift files support standard shell comments.
# This lets you make your thrift file executable and include your Thrift build
# step on the top line. And you can place comments like this anywhere you like.
#
# Before running this file, you will need to have installed the thrift compiler
# into /usr/local/bin.
/**
* The first thing to know about are types. The available types in Thrift are:
*
* bool Boolean, one byte
* i8 (byte) Signed 8-bit integer
* i16 Signed 16-bit integer
* i32 Signed 32-bit integer
* i64 Signed 64-bit integer
* double 64-bit floating point value
* string String
* binary Blob (byte array)
* map<t1,t2> Map from one type to another
* list<t1> Ordered list of one type
* set<t1> Set of unique elements of one type
*
* Did you also notice that Thrift supports C style comments?
*/
// Just in case you were wondering... yes. We support simple C comments too.
/**
* Thrift files can reference other Thrift files to include common struct
* and service definitions. These are found using the current path, or by
* searching relative to any paths specified with the -I compiler flag.
*
* Included objects are accessed using the name of the .thrift file as a
* prefix. i.e. shared.SharedObject
*/
include "shared.thrift"
/**
* Thrift files can namespace, package, or prefix their output in various
* target languages.
*/
namespace java com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial
/**
* Thrift lets you do typedefs to get pretty names for your types. Standard
* C style here.
*/
typedef i32 MyInteger
/**
* Thrift also lets you define constants for use across languages. Complex
* types and structs are specified using JSON notation.
*/
const i32 INT32CONSTANT = 9853
const map<string,string> MAPCONSTANT = {'hello':'world', 'goodnight':'moon'}
/**
* You can define enums, which are just 32 bit integers. Values are optional
* and start at 1 if not supplied, C style again.
*/
enum Operation {
ADD = 1,
SUBTRACT = 2,
MULTIPLY = 3,
DIVIDE = 4
}
/**
* Structs are the basic complex data structures. They are comprised of fields
* which each have an integer identifier, a type, a symbolic name, and an
* optional default value.
*
* Fields can be declared "optional", which ensures they will not be included
* in the serialized output if they aren't set. Note that this requires some
* manual management in some languages.
*/
struct Work {
1: i32 num1 = 0,
2: i32 num2,
3: Operation op,
4: optional string comment,
}
/**
* Structs can also be exceptions, if they are nasty.
*/
exception InvalidOperation {
1: i32 whatOp,
2: string why
}
/**
* Ahh, now onto the cool part, defining a service. Services just need a name
* and can optionally inherit from another service using the extends keyword.
*/
service Calculator extends shared.SharedService {
/**
* A method definition looks like C code. It has a return type, arguments,
* and optionally a list of exceptions that it may throw. Note that argument
* lists and exception lists are specified using the exact same syntax as
* field lists in struct or exception definitions.
*/
void ping(),
i32 add(1:i32 num1, 2:i32 num2),
i32 calculate(1:i32 logid, 2:Work w) throws (1:InvalidOperation ouch),
/**
* This method has a oneway modifier. That means the client only makes
* a request and does not listen for any response at all. Oneway methods
* must be void.
*/
oneway void zip()
}
/**
* That just about covers the basics. Take a look in the test/ folder for more
* detailed examples. After you run this file, your generated code shows up
* in folders with names gen-<language>. The generated code isn't too scary
* to look at. It even has pretty indentation.
*/tutorial.thrift基本介绍:
-
include "shared.thrift"表示tutorial.thrift文件引入了shared.thrift - Java语言的命名空间设置为
namespace java com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial ,也就是说,使用thrift编译器编译上述文件后,生成的代码在上述包中 -
typedef i32 MyInteger 表示用MyInteger表示i32数据类型 - 下述代码表示定义常量
const i32 INT32CONSTANT = 9853
const map<string,string> MAPCONSTANT = {'hello':'world', 'goodnight':'moon'}- 下述代码表示定义枚举
enum Operation {
ADD = 1,
SUBTRACT = 2,
MULTIPLY = 3,
DIVIDE = 4
}- 下述代码表示定义结构
struct Work {
1: i32 num1 = 0,
2: i32 num2,
3: Operation op,
4: optional string comment,
}- 下述代码表示定义异常
exception InvalidOperation {
1: i32 whatOp,
2: string why
}- 下述代码定义基本的服务。表示服务端提供的基本功能。
service Calculator extends shared.SharedService {
/**
* A method definition looks like C code. It has a return type, arguments,
* and optionally a list of exceptions that it may throw. Note that argument
* lists and exception lists are specified using the exact same syntax as
* field lists in struct or exception definitions.
*/
void ping(),
i32 add(1:i32 num1, 2:i32 num2),
i32 calculate(1:i32 logid, 2:Work w) throws (1:InvalidOperation ouch),
/**
* This method has a oneway modifier. That means the client only makes
* a request and does not listen for any response at all. Oneway methods
* must be void.
*/
oneway void zip()
}有了thrift,我们只需要按照thrift接口规范定义好.thrift文件,然后实现其基本功能即可,而不需要关心数据如何传输。
所以,我们定义CalculatorHandler类来实现Calculator服务
/*
* Copyright © 2020 https://www.lrting.top/ All rights reserved.
*/
package com.zh.ch.bigdata.handler;
import com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial.Calculator;
import com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author: bigDataToAi
* @date: 2022/3/21
* @description:
* @modifiedBy:
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class CalculatorHandler implements Calculator.Iface {
private HashMap<Integer,SharedStruct> log;
public CalculatorHandler() {
log = new HashMap<Integer, SharedStruct>();
}
public void ping() {
System.out.println("ping()");
}
public int add(int n1, int n2) {
System.out.println("add(" + n1 + "," + n2 + ")");
return n1 + n2;
}
public int calculate(int logid, Work work) throws InvalidOperation {
System.out.println("calculate(" + logid + ", {" + work.op + "," + work.num1 + "," + work.num2 + "})");
int val = 0;
switch (work.op) {
case ADD:
val = work.num1 + work.num2;
break;
case SUBTRACT:
val = work.num1 - work.num2;
break;
case MULTIPLY:
val = work.num1 * work.num2;
break;
case DIVIDE:
if (work.num2 == 0) {
InvalidOperation io = new InvalidOperation();
io.whatOp = work.op.getValue();
io.why = "Cannot divide by 0";
throw io;
}
val = work.num1 / work.num2;
break;
default:
InvalidOperation io = new InvalidOperation();
io.whatOp = work.op.getValue();
io.why = "Unknown operation";
throw io;
}
SharedStruct entry = new SharedStruct();
entry.key = logid;
entry.value = Integer.toString(val);
log.put(logid, entry);
return val;
}
public SharedStruct getStruct(int key) {
System.out.println("getStruct(" + key + ")");
return log.get(key);
}
public void zip() {
System.out.println("zip()");
}
}接下来我们便可以定义服务端和客户端。
/*
* Copyright © 2020 https://www.lrting.top/ All rights reserved.
*/
package com.zh.ch.bigdata.handler;
import com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial.*;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer.Args;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TSimpleServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerTransport;
/**
* @author: bigDataToAi
* @date: 2022/3/21
* @description:
* @modifiedBy:
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class JavaServer {
public static CalculatorHandler handler;
public static Calculator.Processor processor;
public static void main(String [] args) {
try {
handler = new CalculatorHandler();
processor = new Calculator.Processor(handler);
Runnable simple = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
simple(processor);
}
};
new Thread(simple).start();
} catch (Exception x) {
x.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void simple(Calculator.Processor processor) {
try {
TServerTransport serverTransport = new TServerSocket(9090);
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(new Args(serverTransport).processor(processor));
// Use this for a multithreaded server
// TServer server = new TThreadPoolServer(new TThreadPoolServer.Args(serverTransport).processor(processor));
System.out.println("Starting the simple server...");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}/*
* Copyright © 2020 https://www.lrting.top/ All rights reserved.
*/
package com.zh.ch.bigdata.handler;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSSLTransportFactory;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSSLTransportFactory.TSSLTransportParameters;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import com.zh.ch.bigdata.thrift.tutorial.*;
/**
* @author: bigDataToAi
* @date: 2022/3/21
* @description:
* @modifiedBy:
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class JavaClient {
public static void main(String [] args) {
try {
TTransport transport;
transport = new TSocket("localhost", 9090);
transport.open();
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
Calculator.Client client = new Calculator.Client(protocol);
perform(client);
transport.close();
} catch (TException x) {
x.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void perform(Calculator.Client client) throws TException
{
client.ping();
System.out.println("ping()");
int sum = client.add(1,1);
System.out.println("1+1=" + sum);
Work work = new Work();
work.op = Operation.DIVIDE;
work.num1 = 1;
work.num2 = 0;
try {
int quotient = client.calculate(1, work);
System.out.println("Whoa we can divide by 0");
} catch (InvalidOperation io) {
System.out.println("Invalid operation: " + io.why);
}
work.op = Operation.SUBTRACT;
work.num1 = 15;
work.num2 = 10;
try {
int diff = client.calculate(1, work);
System.out.println("15-10=" + diff);
} catch (InvalidOperation io) {
System.out.println("Invalid operation: " + io.why);
}
SharedStruct log = client.getStruct(1);
System.out.println("Check log: " + log.value);
}
}由上述可知,我们在服务端启动了一个9090端口的thrift服务以监听客户端的请求。于是,便可以在客户端通过连接该端口执行请求。
thrift-maven-plugin使用
在maven项目中使用可以使用如下插件来编译thrift文件从而生成java代码。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-thrift-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.1.11</version>
<configuration>
<thriftExecutable>C:\\softwareInstall\\thrift-0.16.0\\thrift</thriftExecutable>
<thriftSourceRoot>src/main/thrift</thriftSourceRoot>
<outputDirectory>src/main/java</outputDirectory>
<generator>java</generator>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>thrift-sources</id>
<phase>generate-sources</phase>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>在使用上述插件之前,需要先在本地安装thrift编译器,并由thriftExecutable配置项指定。
thrift-example完整代码
https://git.lrting.top/xiaozhch5/thrift-example.git










